Last Updated on December 8, 2023 by Ankit Kochar

Cryptography, the art and science of securing communication, has been a crucial aspect of human history, evolving from ancient techniques to modern digital methods. At its core, cryptography involves the use of mathematical algorithms and principles to convert information into a secure and unreadable format, ensuring confidentiality, integrity, and authentication. In today’s interconnected digital world, cryptography plays a pivotal role in safeguarding sensitive data, enabling secure transactions, and preserving privacy. Understanding the types of cryptography is fundamental to comprehending the mechanisms that underpin secure communication in various domains
What is Cryptography?
Cryptography is the art and science of maintaining secure communication in the presence of potential adversaries. In essence, it revolves around the transformation of information, known as plaintext, into an unreadable format. This transformation is carried out using specific algorithms and methods, resulting in ciphertext that can only be deciphered back into its original form by an authorized party possessing the correct key or knowledge. The primary objective of cryptography is to safeguard information from unauthorized access or interception, ensuring that sensitive data remains confidential and intact during communication.
Cryptography has been used for centuries to secure communication, with the earliest recorded use being the scytale, a rod used by the Ancient Greeks to encrypt messages by wrapping a strip of parchment around it. The invention of the modern computer has made cryptography more important than ever, as it is now used to secure not just military communications but also internet transactions and data storage.
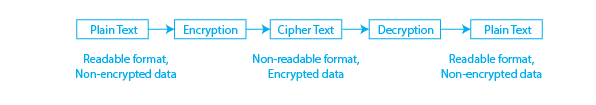
Some Common Cryptography Examples
These are the cryptography examples :
- Secure Web Browsing: When you visit a website with "https" in the URL, the communication between your browser and the website is encrypted using SSL/TLS, which is a form of symmetric key cryptography.
- Online Banking: Many online banking systems use cryptography to secure sensitive financial transactions and protect customers’ personal and financial information.
- Email: Many email services use encryption to protect the privacy and confidentiality of emails in transit. For example, services like Gmail use Transport Layer Security (TLS) to encrypt emails.
- Mobile Devices: Mobile devices, such as smartphones and tablets, often use cryptography to secure data stored on the device and to protect communications. For example, Apple’s iOS uses a hardware encryption system to secure data on iPhones and iPads.
- Cloud Storage: Cryptography is used to secure data stored in the cloud. For example, Amazon Web Services uses the AES encryption algorithm to secure data stored in its Simple Storage Service (S3) and the Amazon Elastic Block Store (EBS).
These are just a few cryptography examples that are widely used in many other areas including VPNs, secure instant messaging, and software updates to name a few
Features of Cryptography
These are the features of cryptography :
- Confidentiality: Hides the contents of a message from unauthorized parties.
- Integrity: Ensures that a message has not been altered during transmission.
- Authentication: Verifies the identity of the sender and receiver of a message.
- Non-repudiation: Prevents the sender from denying having sent a message.
- Availability: Ensures that authorized users have access to the information they need when they need it.
- Key Management: The process of generating, distributing, storing, and replacing cryptographic keys.
- Algorithm: The mathematical formula used to encrypt and decrypt messages.
- Encryption/Decryption: The process of converting plaintext to ciphertext and vice versa.
- Symmetric/Asymmetric Key Encryption: The use of a single shared key for encryption and decryption or the use of a public and private key pair.
- Hash Functions: A one-way mathematical transformation of an input (message) into a fixed-size output (message digest).
- Digital Signatures: A signature that can be used to authenticate the identity of the sender of a message and ensure the integrity of the message.
Types of Cryptography
There are Three Types of Cryptography
Symmetric Key
The symmetric key is a types of cryptography which also known as private key cryptography or secret key cryptography. Both the information receiver and the sender use a single key to encrypt and decrypt the message in this case. it is a method of encryption and decryption that uses a single shared key for both operations. The same key is used to encrypt the plaintext into ciphertext and to decrypt the ciphertext back into plaintext.
AES is the most commonly used type of cryptography in this method (Advanced Encryption System). The approaches used in this type are completely streamlined and faster as well.
Symmetric key cryptography includes the following types:
- Block
- Block cipher
- DES (Data Encryption System)
- RC2
- IDEA
- Blowfish
- Stream cipher
Advantages of Symmetric Key Cryptography include:
- Speed: Encryption and decryption are fast and efficient, making it suitable for large amounts of data.
- Simplicity: The single shared key makes it easier to implement and use compared to asymmetric key cryptography.
Disadvantages of Symmetric Key Cryptography include:
- Key Management: The secure distribution of the shared key between the sender and receiver can be a challenge.
- Scalability: With a large number of users, the number of keys required can quickly become unmanageable.
- Security: If the shared key is compromised, the confidentiality and integrity of the data can be threatened.
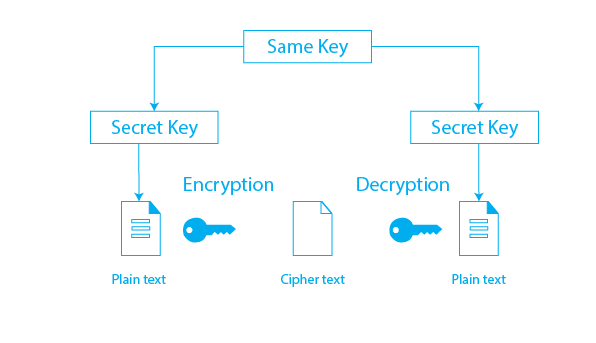
Asymmetric Key
The asymmetric key is types of cryptography which also known as public-key cryptography. It employs a diverse and secure method of information transmission. The most common type of cryptography used in this method is RSA. An asymmetric key refers to a cryptographic method that uses two different keys for encryption and decryption. The two keys are called the public key and the private key. The public key is used to encrypt the data and the private key is used to decrypt it. The security of this method is based on the fact that it is computationally infeasible to derive the private key from the public key. Asymmetric key cryptography is commonly used for secure communication, digital signatures, and public key infrastructure (PKI).
Asymmetric Key Cryptography includes the following types:
- RSA
- DSA
- PKCs
Advantages of Asymmetric Key Cryptography:
- Increased security: The use of two different keys makes it more secure than symmetric key cryptography.
- Non-repudiation: The digital signature created using the private key provides proof of the authenticity of the sender.
- Scalability: Asymmetric key cryptography can support a large number of users.
- Public key distribution: The public key can be freely distributed without any security risk, allowing for easy encryption of messages.
Disadvantages of Asymmetric Key Cryptography:
- Computational overhead: The encryption and decryption process using asymmetric key cryptography is slower and more resource-intensive compared to symmetric key cryptography.
- Key management: Asymmetric key cryptography requires the safekeeping and management of both private and public keys.
- Key length: The security of asymmetric key cryptography is directly proportional to the length of the key used. Longer keys require more processing power, making them less practical for some applications.
- Lack of standardization: Asymmetric key cryptography is still evolving and there is a lack of standardization in terms of algorithms and key lengths, making it difficult for interoperability between different systems

Hash Function
Types of cryptography in which an algorithm followed by a hash function take an arbitrary length of the message as input and returns a fixed length of the output. It is also referred to as a mathematical equation because it uses numerical values as input to generate the hash message. This method does not require a key because it operates in a one-way scenario. Each round of hashing operations considers input as an array of the most recent block and generates the last round of activity as output.
Some of the hash’s features include:
- Message Digest 5 (MD5)
- RIPEMD
- Whirlpool
- SHA (Secure hash Algorithm)
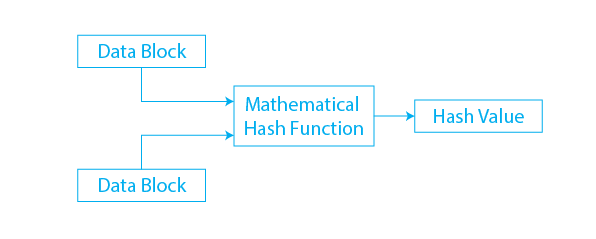
Applications of Cryptography
These are the application of Cryptography:
- Secure Communications: Cryptography is widely used to secure communications over the internet, such as email, instant messaging, and virtual private networks (VPNs).
- Data Protection: Cryptography is used to protect sensitive data, such as financial information, medical records, and government secrets, from unauthorized access,all these are cryptography examples.
- E-commerce and Online Transactions: Cryptography is used to secure online transactions, such as online shopping and banking, to protect sensitive information and prevent fraud.
- Authentication: Cryptography is used to authenticate the identity of users and devices, such as digital certificates, biometric authentication, and smart cards.
- Cloud Computing: Cryptography is used to secure cloud computing services, such as data storage and processing, by encrypting data and controlling access.
- Wireless Networks: Cryptography is used to secure wireless networks, such as Wi-Fi, from unauthorized access and data interception.
- Disk Encryption: Cryptography is used to secure data stored on disk drives, such as full-disk encryption and encrypted file systems, to prevent unauthorized access.
- Mobile Devices: Cryptography is used to secure mobile devices, such as smartphones and tablets, to protect sensitive data and prevent unauthorized access.
- Digital Rights Management: Cryptography is used to protect the rights of copyright holders by controlling the distribution and usage of digital content, such as music, movies, and software.
Conclusion
Cryptography serves as the bedrock of secure communication in the digital era, providing the tools and techniques necessary to protect information from unauthorized access and tampering. Whether it’s safeguarding financial transactions, securing sensitive communications, or preserving user privacy, the various types of cryptography play pivotal roles in ensuring the integrity and confidentiality of data. As technology continues to advance, cryptography remains a dynamic field, adapting to new challenges and evolving threat landscapes. Understanding its principles and types is essential for individuals and organizations seeking to navigate the complex landscape of digital security.
Some common types of cryptography are:
- symmetric-key cryptography
- asymmetric-key cryptography
- Hashing.
Cryptography involves the use of mathematical algorithms and protocols to encode, transmit and decode data, and often relies on secret keys to ensure its security.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) related to Cryptography and its types
Here are some Frequently Asked Questions related to “Cryptography and Types of Cryptography”.
1. What is cryptography, and why is it important in the digital age?
Cryptography is the science of securing communication through the use of codes and ciphers. In the digital age, it is crucial for ensuring the confidentiality and integrity of data, protecting against unauthorized access and cyber threats.
2. What are the main types of cryptography?
The main types of cryptography include symmetric-key cryptography, asymmetric-key cryptography (public-key cryptography), and hash functions.
3. How does symmetric-key cryptography work?
Symmetric-key cryptography uses a single key for both encryption and decryption. The same key is shared between the communicating parties, and maintaining the secrecy of this key is critical for secure communication.
4. What is asymmetric-key cryptography, and how does it differ from symmetric-key cryptography?
Asymmetric-key cryptography uses a pair of keys – a public key for encryption and a private key for decryption. Unlike symmetric-key cryptography, the public key can be shared openly, allowing secure communication without a prior exchange of secret keys.
5. What is the role of public-key infrastructure (PKI) in asymmetric-key cryptography?
Public-key infrastructure manages the generation, distribution, and revocation of public and private key pairs, ensuring the integrity and authenticity of public keys in asymmetric-key cryptography.


