Last Updated on August 9, 2023 by Mayank Dham

Counters in Digital electronics serve as crucial hardware components and are defined as "Digital circuits employed for tallying pulses." These components are commonly known as "Timers" in everyday language. Counter circuits provide an excellent illustration of flip-flop utilization. Counters are formed by grouping flip flops together and providing them with a unified clock signal. Put simply, counters utilize a collection of storage elements like flip flops to monitor the tally.
Digital circuits known as counters are capable of enumerating events or the pulses within a signal. These counters find utility in diverse digital applications, including digital clocks, time measurement, and frequency assessment. In the subsequent section, we will delve into the realm of counters in digital electronics, exploring the various counter types, and their applications, and addressing frequently encountered queries regarding these devices.
What are Counters in Digital Electronics?
A counter in digital electronics constitutes a device that retains (and occasionally presents) the numerical occurrence of a designated event or procedure, often synchronized with a clock signal. These instruments find application in digital electronics to enumerate specific incidents transpiring within a circuit. For instance, a UP counter registers an increment with each ascending clock edge. Beyond simple counting, a counter can conform to a predetermined sequence as per our design, encompassing arbitrary patterns like 0, 1, 3, 2… The utilization of flip-flops aids in the formation of counters.
Counters fulfill the role of frequency dividers, partitioning the frequency of a given pulse waveform. Functioning as sequential circuits, counters tabulate pulse quantities in either binary or BCD formats. The key attributes of a counter encompass timing, sequencing, and enumeration. This device operates in dual modes.
Types of Counters in Digital Electronics
The Counters in digital electronics are broadly classified into two main categories :
1) Asynchronous Counters
The asynchronous counter is also called as Ripple counter and is made up of a series of flip-flops. If the flip-flops do not receive the same clock signal, the counter is referred to as asynchronous. Only the first flip-flop receives a clock signal from the system clock. The remaining flip-flops receive the clock signal from the previous stage flip-output.
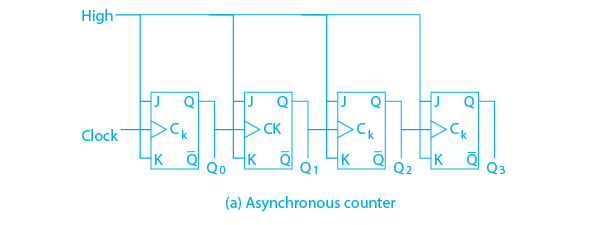

The timing diagram clearly shows that Q0 changes as soon as the rising edge of the clock pulse is encountered, Q1 changes when the rising edge of Q0 is encountered (because Q0 is like the clock pulse for the second flip-flop), and so on. Because ripples are generated in this manner by Q0, Q1, Q2, and Q3, it is also known as a RIPPLE counter and a serial counter. A ripple counter is a cascaded configuration of flip-flops in which the output of one flip-flop drives the clock input of the flip-flop after it.
2) Synchronous Counters
The synchronous counter is a counter also known as the parallel counter, operation is fast if we compare it with asynchronous counters. The synchronous counter has a single global clock that drives each flip-flop, allowing output to change in parallel. The synchronous counter can operate at higher frequencies, In the synchronous counter, all of the flip flops clock inputs use the same source and produce the output at the same time. The synchronous counter produces fewer errors than the asynchronous counter.
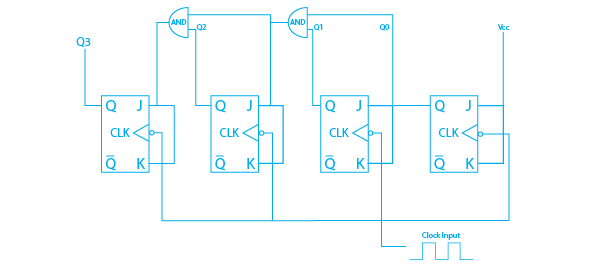

From the circuit diagram, we see that the Q0 bit gives a response to each falling edge of the clock while Q1 is dependent on Q0, Q2 is dependent on Q1 and Q0, and Q3 is dependent on Q2, Q1, and Q0.
Application of Counters in Digital Electronics
Here are the applications of the counters in digital electronics:
-
Frequency Measurement and Division
The counter is used to measure the frequency of a signal, simply by counting the no of cycles in a particular given time period and the counter is also used to divide the input clock frequency by a fixed integer value. -
Timing
The counter is also used to generate timing signals like pulse-width modulated (PWM) signals. These signals are commonly used in power electronics to control the speed of motors and regulate the brightness of LEDs. -
Binary Arithmetic
Binary arithmetic operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division are used in digital systems by counters. -
Data Storage
Counters can also be used as memory elements in a digital circuit if take an example of a binary operator. The binary counter can be used to store a binary value that represents a state in a digital system. -
Digital Signal Processing
Counters are also used in digital signal processing applications like filtering and signal analysis.
Conclusion
In conclusion, counters in digital electronics represent digital circuits or devices designed to retain (and at times exhibit) the number of occurrences of a distinct event or operation, usually synchronized with a clock signal. These counters are harnessed in digital electronics to tally particular happenings within a circuit. Broadly, two categories of counters exist: synchronous counters, alternatively known as parallel counters, and asynchronous counters, also referred to as Ripple counters. Counters in digital electronics find utility in various applications, including frequency measurement and division, timing functions, data retention, digital signal processing, and more.
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQ):
Q1. What is the basic aspect of a counter?
Ans. The basic principle of a counter is to count the number of occurrences of a specific signal or event by incrementing a binary counter each time the signal is detected.
Q2. What is a binary counter?
Ans. It is a type of counter that counts in binary, That is, it can only count up to a certain maximum number of bits before winding around and begin over from zero.
Q3. What is a ripple counter?
Ans. A ripple counter is a type of binary counter that uses a series of flip-flops to count each bit in the binary sequence.
Q4. What is a decade counter?
Ans. A decade counter is a type of counter that counts in decimal, meaning it can count up to ten before wrapping around and starting over.
Q5. What is a Johnson counter?
Ans. A Johnson counter is a type of ring counter that uses feedback to create a sequence that can count signals.
Q6. What is a digital timer?
Ans. A digital timer is a device that uses a counter to measure the duration of an event or time interval.
Q7. What is a pulse counter?
Ans. A pulse counter is a device that counts the number of pulses or events that occur over a specific time period.


