Last Updated on November 23, 2023 by Ankit Kochar

In the realm of data structures, heaps stand out as an essential tool for efficient manipulation of priority-based information. One common problem encountered when dealing with heaps is finding the Kth largest element within them. Whether it’s a min-heap or a max-heap, determining the Kth largest element involves specific techniques that leverage the structure’s properties to optimize the search.
This article delves into the intricacies of finding the Kth largest element in a heap, exploring various approaches and algorithms tailored for different types of heaps. From understanding the fundamentals of heaps to implementing algorithms for extracting the Kth largest element, this guide aims to provide a comprehensive overview of this problem-solving process. Basically, Given the heights of N buildings and an integer k, we have to find the height of kth highest building.
See original problem statement here
How to Find Kth Largest Element?
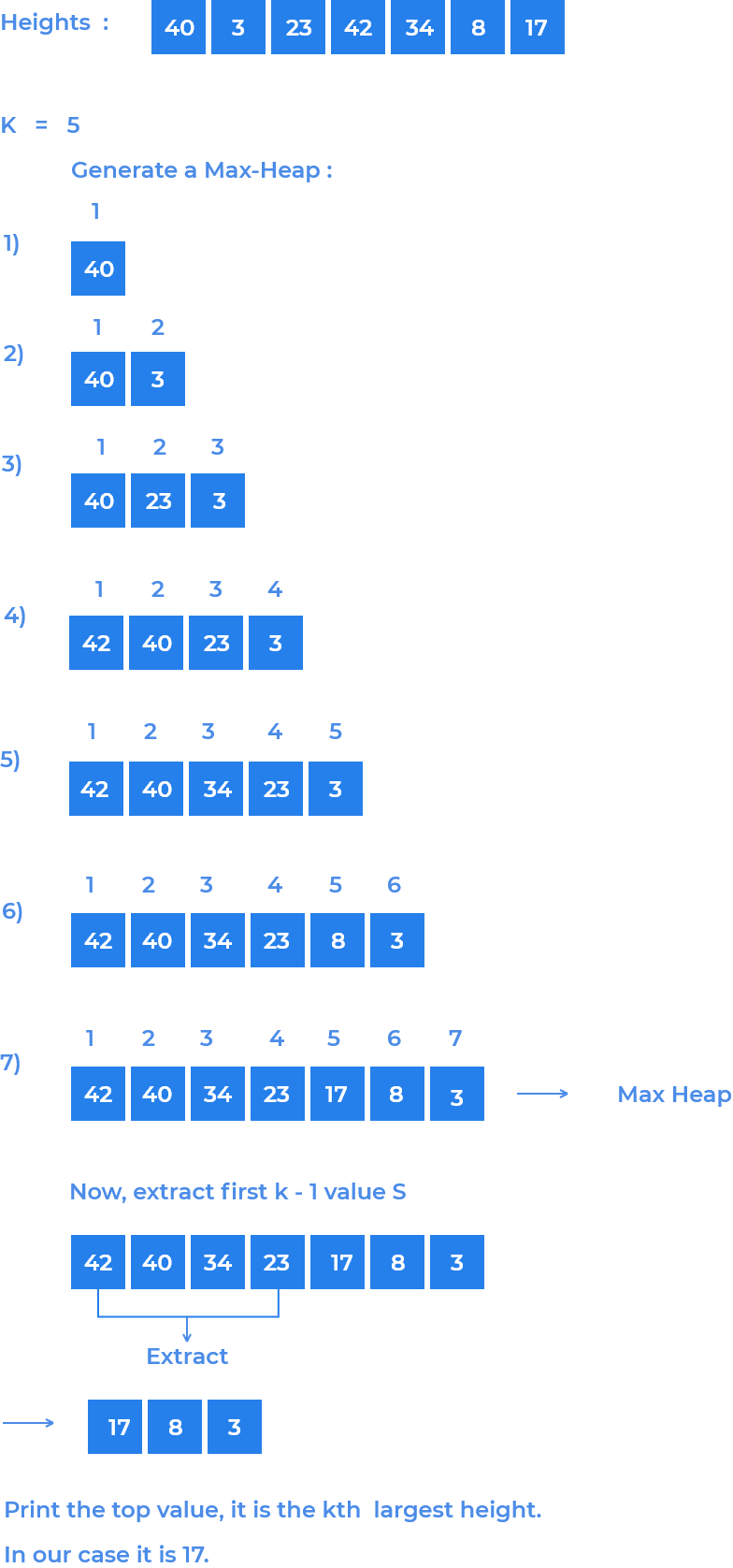
Idea is to create a max-heap of heights of buildings, in order to get kth highest height we need go remove first
k-1largest height.
Method 1 :
Sort the array containing heights of the buildings in decreasing order using any sorting algorithm. Now print the kth value in the array which is the kth highest height.
Method 2 :
-
Geneate a max-heap from the heights of the buildings.
-
In a max-heap, the root always stores the larger value as compared to its left & right subtree, this condition needs to be true for every node. We need to insert each item one by one such that parent is always larger than the item itself. If parent is smaller, then swap the current item with its parent.
-
After generating max-heap now extract first
k-1heights from the heap. Among the remaining heights, the first element of the heap (heap[0]) is thekthhighest element.
extract(): Removes the maximum element from Max-Heap. Time Complexity of this Operation is O(Logn) as this operation needs to maintain the heap property (by calling heapify()) after removing root.
heapify(): Maintains the heap property for each node. If any node does not follow heap property it swaps the node with the node which is smaller ,or greater (in case of max-heap), than the node.
Algorithms :
Insert() :
- Insert the item at the last index, and increment the size by 1.
- Then, check if the inserted item is smaller than its parent,
- If yes, then swap the inserted item with its parent.
- If no, then do nothing.
- Now, go to step
2and repeat untill we reach root (first element).
Extract() :
- Store the value of the first node of our heap (
temp = heap[0]).- Replace the root node with the farthest right node (last element).
- Decrease the size by
1.(heap[0] = heap[size-1])- Perform heapify starting from the new root.
- Return the stored value (
temp).
Heapify ():
- if the heap property holds true then you are done.
- else if
- the replacement node value < its parent nodes value
then swap them, and repeat step 3.- else
- swap the replacement node with the largest child node, and
repeat step 3.
Example:
Solutions:
#include<stdio.h>
void swap(int *a, int *b)
{
*a = *a + *b;
*b = *a - *b;
*a = *a - *b;
}
void minHeapify(int a[], int size, int i)
{
int l = 2*i+1;
int r = 2*i+2;
int smallest = i;
if(l<size && a[l]<a[smallest])
smallest = l;
if(r<size && a[r]<a[smallest])
smallest = r;
if(smallest!=i)
{
swap(&a[i],&a[smallest]);
minHeapify(a,size,smallest);
}
}
void buildMinHeap(int a[], int size) {
for(int i=size/2;i>=0;i--)
minHeapify(a,size,i);
}
int kthLargest(int a[], int size, int k)
{
int minHeap[k];
int i;
for(i=0;i<k;i++)
minHeap[i] = a[i];
buildMinHeap(minHeap,k);
for(i=k;i<size;i++)
{
if(a[i]>minHeap[0])
{
minHeap[0]=a[i];
minHeapify(minHeap,k,0);
}
}
return minHeap[0];
}
int main() {
int t;
scanf("%d",&t);
while(t--)
{
int n,k;
scanf("%d %d",&n,&k);
int a[n+1];
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
printf("%d\n",kthLargest(a,n,k));
}
return 0;
}
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int parent(int i)
{
return (i-1)/2;
}
int left(int i)
{
return (i*2)+1;
}
int right(int i)
{
return (i*2)+2;
}
void swap(int *a,int *b)
{
int temp = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = temp;
}
void insert(int heap[],int *size, int val)
{
heap[*size]= val;
int i = *size;
(*size)++;
while(i!=0 && heap[parent(i)]>heap[i])
{
swap(&heap[parent(i)],&heap[i]);
i = parent(i);
}
}
void heapify(int heap[],int i,int size)
{
int l = left(i);
int r = right(i);
int lar = i;
if(lar<size && heap[l]<heap[i])
lar = l;
if(r<size && heap[r]<heap[lar])
lar = r;
if(lar!=i)
{
swap(&heap[i],&heap[lar]);
heapify(heap,lar,size);
}
}
int extract(int heap[],int *size)
{
int root = heap[0];
heap[0] = heap[*size-1];
(*size)--;
heapify(heap,0,*size);
return root;
}
int main()
{
int t;
cin>>t;
while(t--)
{
int n,k;
cin>>n>>k;
int *heap = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int)*n);
int size = 0;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
int t;
cin>>t;
insert(heap,&size,t);
}
while(--k)
{
extract(heap,&size);
}
cout<<extract(heap,&size)<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class Main {
static int size = 0;
public int findKthLargest(int[] nums, int k) {
this.size = nums.length;
int ans = 0;
int last = (this.size-1)/2;
for(int i=last;i>=0;i--)
downheapify(nums,i);
for(int i=1;i<=k;i++)
ans = remove(nums);
return ans;
}
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int t = sc.nextInt();
while(t-->0)
{
Main m = new Main();
int n= sc.nextInt();
int k = sc.nextInt();
int []a = new int[n];
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{a[i]= sc.nextInt();}
System.out.println(m.findKthLargest(a,k));
}
}
public void swap(int []nums,int i, int j) {
int temp = nums[i];
nums[i] = nums[j];
nums[j] = temp;
}
public int remove(int []nums) {
swap(nums,0,this.size - 1);
int temp = nums[this.size - 1];
this.size--;
downheapify(nums,0);
return temp;
}
public void downheapify(int []nums,int pi) {
int mini = pi;
int li = 2 * pi + 1;
int ri = 2 * pi + 2;
if (li < this.size && nums[li] > nums[mini])
mini = li;
if (ri < this.size && nums[ri] > nums[mini])
mini = ri;
if (mini != pi) {
swap(nums,mini, pi);
downheapify(nums,mini);
}
}
}
[forminator_quiz id="1608"]
Conclusion
In conclusion, the quest to find the Kth largest element in a heap unveils a blend of concepts from heap data structures and algorithms for efficient traversal and extraction. By leveraging the properties inherent in heaps – be it a min-heap or max-heap – specific algorithms have been designed to swiftly identify and extract the Kth largest element.
Understanding the principles governing heaps, exploring efficient traversal techniques, and applying suitable algorithms tailored to the type of heap at hand are key to successfully solving this problem. As demonstrated, mastering these concepts empowers developers and computer scientists to optimize their code and tackle similar challenges in diverse applications.
FAQ Related to the Kth Largest Element using Heap:
Here are some FAQs related to Kth Largest Element using Heap.
1. What is a heap in data structures?
A heap is a specialized tree-based data structure that satisfies the heap property. In a min-heap, for any given node, the value of the node is less than or equal to the values of its children. Conversely, in a max-heap, the value of the node is greater than or equal to its children’s values.
2. How do you find the Kth largest element in a heap?
To find the Kth largest element in a heap, you can perform a traversal and extraction approach. For a max-heap, you can iteratively extract the maximum element K times, resulting in the Kth largest element. For a min-heap, you can convert it into a max-heap or use a different approach like traversing the heap to identify the Kth largest element efficiently.
3. Can the Kth largest element be found efficiently in a heap?
Yes, the Kth largest element can be found efficiently in a heap using various algorithms. These approaches often take advantage of heap properties, such as heapifying or performing traversals with optimized time complexities, achieving efficient extraction of the Kth largest element.
4. What are the applications of finding the Kth largest element in a heap?
Finding the Kth largest element in a heap has applications in various domains, including algorithms for finding medians, solving problems related to priority queues, optimizing search algorithms, and in scenarios requiring efficient extraction of top-K elements from a dataset.


