Last Updated on March 31, 2022 by Ria Pathak

Concepts Used
Breadth First Search
Difficulty Level
Hard
Problem Statement :
Given a graph we have to find the length of the shortest cycle in the given graph. If no cycle exists print
−1.
See original problem statement here
Solution Approach :
Introduction :
Idea is to check the length of the cycle from every vertex and print the minimum length, if no cycle is present print
-1.We can use BFS to store the cycle length for every vertex.
Description :
We will iterate for all vertices and store distance and parent of every vertex v using distance[ ] and parent[ ] array. Now for every v iterate for all its adjacent vertices a, if a is not visited update its distance (distance[a] = distance[v]+1) and parent (parent[a] = v). If a is already visited check if parent[a] is v or not, if not then there is a cycle. Now update the minimum cycle length if the current cycle length is shorter.
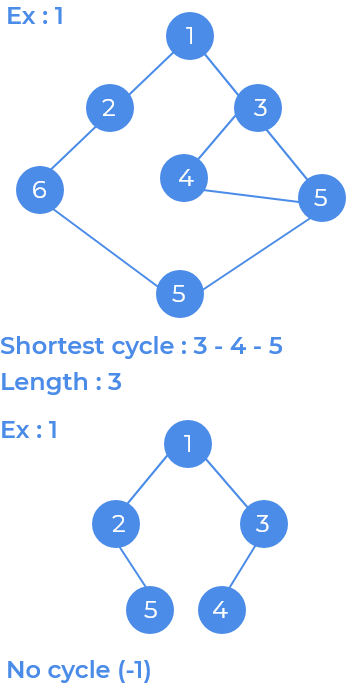
Algorithms :
shortest_cycle() :
-
create a queue and push the current vertex now perform following operations untill the queue is not empty:
-
each time we pop a vertex
vfrom queue, (v= queue.front() ), we will mark the vertexvas visited (visited[v]= true). -
Iterate for all the adjacent vertices of
vand for every adjacent vertexa, do following :- update the parent and distance as,
parent[a] = vanddistance[a]= distance[v]+1. - push
ainto the queue. - if
ais not visited,
and ifparent[v] != a. - update the ans ( ans = min(ans,current cycle length) ).
- update the parent and distance as,
Complexity Analysis:
The time complexity of the above method is represented in the form of
O(V+E), whereVis the number of verices andEis the number of edges.
Solutions:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
#define INT_MAX 99999
#define INT_MIN -99999
//ADJACENCY LIST
struct node {
int vertex;
struct node* next;
};
struct node* createNode(int);
struct Graph {
int numVertices;
struct node** adjLists;
};
// Create a node
struct node* createNode(int v) {
struct node* newNode = malloc(sizeof(struct node));
newNode->vertex = v;
newNode->next = NULL;
return newNode;
}
// Create a graph
struct Graph* createAGraph(int vertices) {
struct Graph* graph = malloc(sizeof(struct Graph));
graph->numVertices = vertices;
graph->adjLists = malloc(vertices * sizeof(struct node*));
int i;
for (i = 0; i < vertices; i++)
graph->adjLists[i] = NULL;
return graph;
}
// Add edge
void addEdge(struct Graph* graph, int s, int d) {
// Add edge from s to d
struct node* newNode = createNode(d);
newNode->next = graph->adjLists[s];
graph->adjLists[s] = newNode;
// Add edge from d to s
newNode = createNode(s);
newNode->next = graph->adjLists[d];
graph->adjLists[d] = newNode;
}
// Print the graph
void printGraph(struct Graph* graph) {
int v;
for (v = 0; v < graph->numVertices; v++)
{
struct node* temp = graph->adjLists[v];
//printf("\n Vertex %d\n: ", v);
while (temp) {
printf("%d ", temp->vertex);
temp = temp->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
}
//QUEUE
struct Queue
{
int front, rear, size;
unsigned capacity;
int* array;
};
// function to create a queue of given capacity.
// It initializes size of queue as 0
struct Queue* createQueue(unsigned capacity)
{
struct Queue* queue = (struct Queue*) malloc(sizeof(struct Queue));
queue->capacity = capacity;
queue->front = queue->size = 0;
queue->rear = capacity - 1; // This is important, see the enqueue
queue->array = (int*) malloc(queue->capacity * sizeof(int));
return queue;
}
// Queue is full when size becomes equal to the capacity
int isFull(struct Queue* queue)
{ return (queue->size == queue->capacity); }
// Queue is empty when size is 0
int isEmpty(struct Queue* queue)
{ return (queue->size == 0); }
// Function to add an item to the queue.
// It changes rear and size
void enqueue(struct Queue* queue, int item)
{
if (isFull(queue))
return;
queue->rear = (queue->rear + 1)%queue->capacity;
queue->array[queue->rear] = item;
queue->size = queue->size + 1;
}
// Function to remove an item from queue.
// It changes front and size
int dequeue(struct Queue* queue)
{
if (isEmpty(queue))
return INT_MIN;
int item = queue->array[queue->front];
queue->front = (queue->front + 1)%queue->capacity;
queue->size = queue->size - 1;
return item;
}
// Function to get front of queue
int front(struct Queue* queue)
{
if (isEmpty(queue))
return INT_MIN;
return queue->array[queue->front];
}
int min(int a,int b)
{
return (a<b)?a:b;
}
int shortest_cycle(struct Graph* graph,int n)
{
// To store length of the shortest cycle
int ans = INT_MAX;
// For all vertices
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// Make distance maximum
int dist[n];
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
dist[i]=INT_MAX;
// Take a imaginary parent
int par[n] ;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
par[i]= -1;
// Distance of source to source is 0
dist[i] = 0;
struct Queue* q = createQueue(1000);
// Push the source element
enqueue(q,i);
// Continue until queue is not empty
while (!isEmpty(q)) {
// Take the first element
int x = front(q);
dequeue(q);
// Traverse for all it's childs
struct node* temp = graph->adjLists[x];
while(temp) {
// If it is not visited yet
if (dist[temp->vertex] == INT_MAX) {
// Increase distance by 1
dist[temp->vertex] = 1 + dist[x];
// Change parent
par[temp->vertex] = x;
// Push into the queue
enqueue(q,temp->vertex);
}
// If it is already visited
else if (par[x] != temp->vertex)
ans = min(ans, dist[x] + dist[temp->vertex] + 1);
temp = temp->next;
}
}
}
// If graph contains no cycle
if (ans == INT_MAX)
return -1;
// If graph contains cycle
else
return ans;
}
int main()
{
int t;
scanf("%d",&t);
while(t--)
{
int n ,e;
scanf("%d %d",&n,&e);
struct Graph* graph = createAGraph(n);
while(e--)
{
int u,v;
scanf("%d %d",&u,&v);
addEdge(graph, u,v);
}
printf("%d\n",shortest_cycle(graph,n));
}
return 0;
}
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define N 10000
vector<int> gr[N];
// Function to add edge
void Add_edge(int x, int y)
{
gr[x].push_back(y);
gr[y].push_back(x);
}
// Function to find the length of
// the shortest cycle in the graph
int shortest_cycle(int n)
{
// To store length of the shortest cycle
int ans = INT_MAX;
// For all vertices
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// Make distance maximum
vector<int> dist(n, INT_MAX);
// Take a imaginary parent
vector<int> par(n, -1);
// Distance of source to source is 0
dist[i] = 0;
queue<int> q;
// Push the source element
q.push(i);
// Continue until queue is not empty
while (!q.empty()) {
// Take the first element
int x = q.front();
q.pop();
// Traverse for all it's childs
for (int child : gr[x]) {
// If it is not visited yet
if (dist[child] == INT_MAX) {
// Increase distance by 1
dist[child] = 1 + dist[x];
// Change parent
par[child] = x;
// Push into the queue
q.push(child);
}
// If it is already visited
else if (par[x] != child)
ans = min(ans, dist[x] + dist[child] + 1);
}
}
}
// If graph contains no cycle
if (ans == INT_MAX)
return -1;
// If graph contains cycle
else
return ans;
}
int main()
{
int t;
cin>>t;
while(t--)
{
int n ,e;
cin>>n>>e;
for(int i=0;i<e;i++)
gr[i].clear();
while(e--)
{
int u,v;
cin>>u>>v;
Add_edge(u,v);
}
cout <<shortest_cycle(n)<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
import java.util.*;
class Main
{
static final int N = 100200;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
static Vector<Integer>[] gr = new Vector[N];
// Function to add edge
static void Add_edge(int x, int y)
{
gr[x].add(y);
gr[y].add(x);
}
// Function to find the length of
// the shortest cycle in the graph
static int shortest_cycle(int n)
{
// To store length of the shortest cycle
int ans = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
// For all vertices
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
// Make distance maximum
int[] dist = new int[n];
Arrays.fill(dist, (int) 1e9);
// Take a imaginary parent
int[] par = new int[n];
Arrays.fill(par, -1);
// Distance of source to source is 0
dist[i] = 0;
Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList<>();
// Push the source element
q.add(i);
// Continue until queue is not empty
while (!q.isEmpty())
{
// Take the first element
int x = q.poll();
// Traverse for all it's childs
for (int child : gr[x])
{
// If it is not visited yet
if (dist[child] == (int) (1e9))
{
// Increase distance by 1
dist[child] = 1 + dist[x];
// Change parent
par[child] = x;
// Push into the queue
q.add(child);
}
else if (par[x] != child && par[child] != x)
ans = Math.min(ans, dist[x] + dis[child] + 1);
}
}
}
// If graph contains no cycle
if (ans == Integer.MAX_VALUE)
return -1;
// If graph contains cycle
else
return ans;
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int t = sc.nextInt();
while(t-->0)
{
int n = sc.nextInt();
int e = sc.nextInt();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
gr[i] = new Vector<>();
while(e-->0)
{
int u = sc.nextInt();
int v = sc.nextInt();
Add_edge(u,v);
}
// Function call
System.out.println(shortest_cycle(n));
}
}
}
[forminator_quiz id="2125"]
This article tried to discuss Breadth First Search. Hope this blog helps you understand and solve the problem. To practice more problems on Breadth First Search you can check out MYCODE | Competitive Programming.


