Last Updated on July 27, 2023 by Mayank Dham

Bubble Sort, renowned for its simplicity and elegance, stands as one of the earliest sorting algorithms. While traditionally used with arrays, this classic method gracefully extends its functionality to Linked Lists. In this concise exploration, we uncover the mechanics, advantages, and limitations of applying Bubble Sort in Linked Lists, appreciating its efficiency and timeless appeal in computer science.
What is Bubble sort?
Bubble sort is a simple and commonly used sorting algorithm in computer science. It is named "bubble sort" because smaller elements "bubble" to the top of the list while larger elements gradually "sink" to the bottom. It is an iterative algorithm that repeatedly steps through the list, compares adjacent elements, and swaps them if they are in the wrong order.
Bubble Sort by Swapping Nodes in Linked List
Swapping Nodes using Bubble Sort in Linked List
In this problem, we are given a singly linked list. We have to sort this list using bubble sort.
Note: The bubble sort will be applied on nodes instead of values i.e., We have to swap the nodes instead of values.
Understanding the working of Bubble Sort in Linked List
Let’s try to understand the problem statement with the help of examples by referring the best websites to learn coding.
Suppose the given list is 5 → 1 → 4 → 2 → 8.
- According to the problem statement, we have to sort the given list using bubble sort.
- What do we usually do? We usually swap the node data. But here, we have to swap the nodes and not their data.
- In the first step, suppose we have to swap 5 and 1. So, we will swap the nodes and not their data. So, the linked list after the first step will be 1 → 5 → 4 → 2 → 8. In this way, swapping will happen, and our final sorted linked list will be 1 → 2 → 4 → 5 → 8
Input:
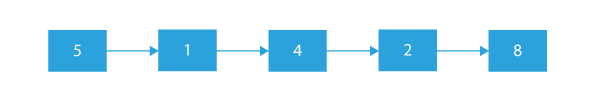
Output:

Explanation: As we can see, the given singly linked list has been sorted.
This question is not a very complex one. We have to apply a normal bubble sort on the list. The only difference is that instead of swapping the data of adjacent nodes, we will swap the nodes. Let us have a glance at the approach.
Approach and Algorithm of bubble sort in linked list
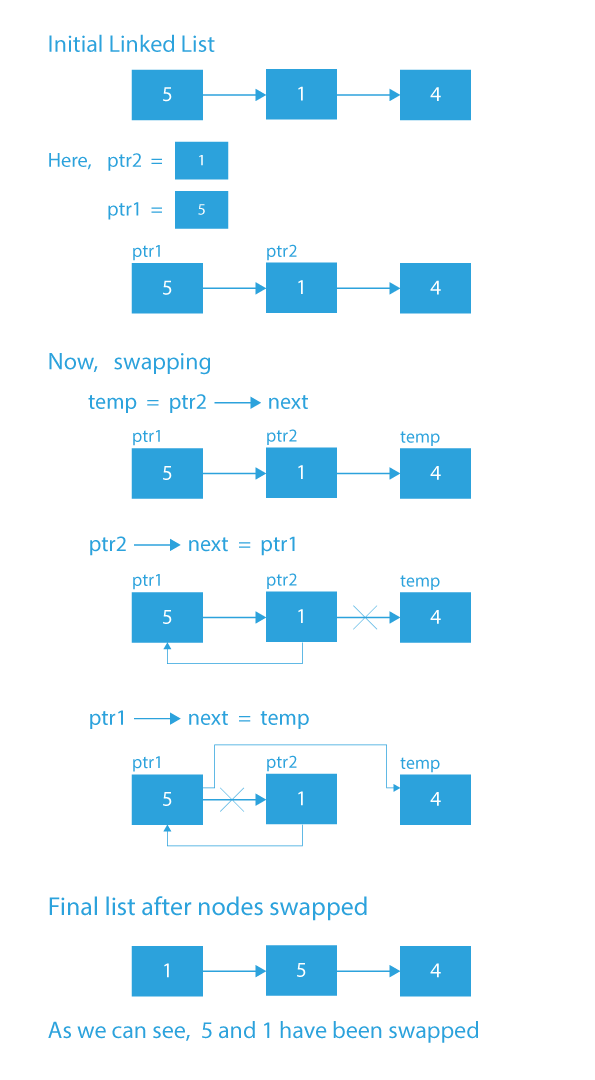
Swap() function
In the swap() function, we will see how we can swap two adjacent nodes.
- Let the two adjacent nodes be p1 and p2.
- Now we will create 2 pointers ptr1 and ptr2, and will make ptr1 point to p1 and ptr2 point to p2.
- Next, we will create a pointer temp, and will make it point to the next of ptr2.
- We will make the next of ptr2 point to ptr1 and next of ptr1 point to temp.
- In this way, following the above steps, the two adjacent nodes p1 and p2 will get swapped.
Dry Run (Swap() function)
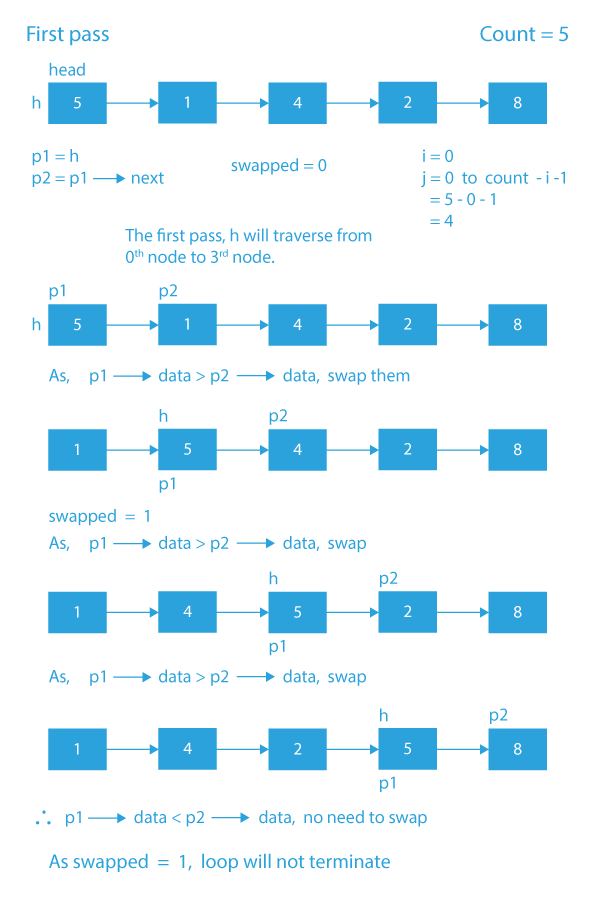
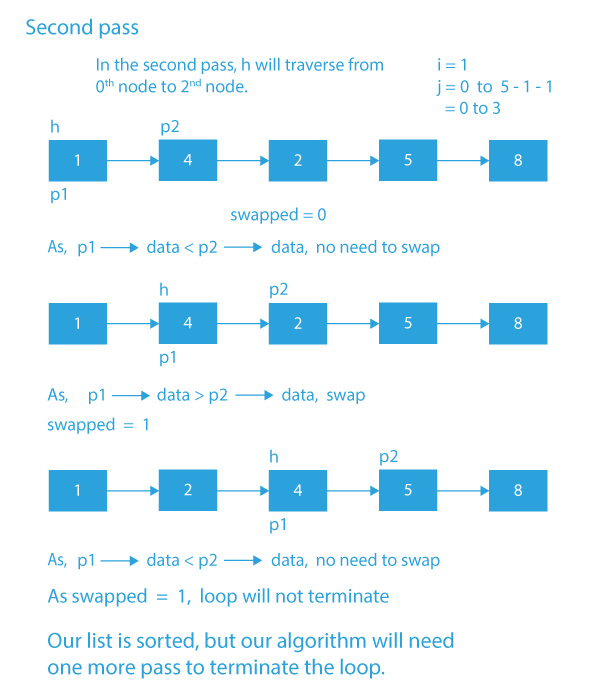
BubbleSort()
In this method, we will see how to perform Bubble Sort on the linked list.
- First, we need the count of the number of nodes in the list. The count can be found with a single list traversal.
- Now, the first loop is going to run from 0 to count-1.
- Inside the first loop, we will create a node pointer h that will point to the head and a variable swapped, initializing it with 0.
- The nested loop will run from 0 to count-i-1.
- Inside the nested loop, we will check if the adjacent elements are following ascending order or not.
- If any pair of adjacent nodes are not following the ascending order, we will swap the nodes and the value of swapped will become 1.
- After the above, if condition, we will increment the h.
- Now, after the inner loop, if the value of the variable swapped remains 0, it means that the list is sorted, and we will break the loop. Otherwise we will continue with the loop.
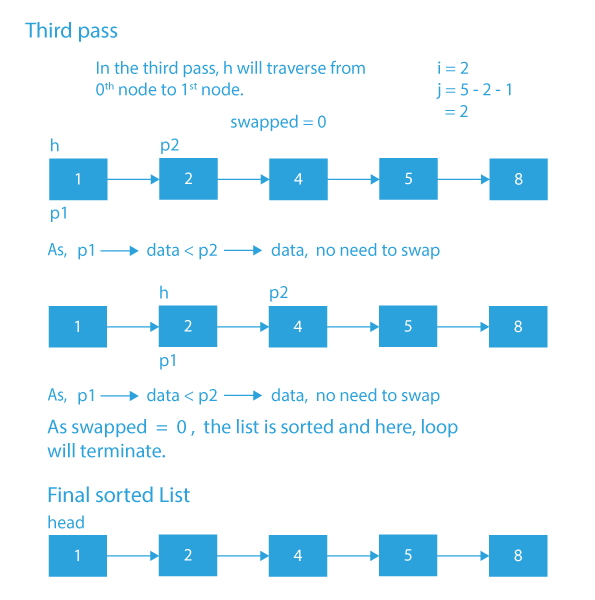
Dry Run of Bubble sort
Code Implementation of bubble sort in linked list
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
/* structure for a node */
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node* next;
} Node;
/*Function to swap the nodes */
struct Node* swap(struct Node* ptr1, struct Node* ptr2)
{
struct Node* tmp = ptr2->next;
ptr2->next = ptr1;
ptr1->next = tmp;
return ptr2;
}
/* Function to sort the list */
int bubbleSort(struct Node** head, int count)
{
struct Node** h;
int i, j, swapped;
for (i = 0; i <= count; i++) {
h = head;
swapped = 0;
for (j = 0; j < count - i - 1; j++) {
struct Node* p1 = *h;
struct Node* p2 = p1->next;
if (p1->data > p2->data) {
/* update the link after swapping */
*h = swap(p1, p2);
swapped = 1;
}
h = &(*h)->next;
}
/* break if the loop ended without any swap */
if (swapped == 0)
break;
}
}
/* Function to print the list */
void printList(struct Node* n)
{
while (n != NULL) {
printf("%d -> ", n->data);
n = n->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
/* Function to insert a struct Node
at the beginning of a linked list */
void insertAtTheBegin(struct Node** start_ref, int data)
{
struct Node* ptr1
= (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
ptr1->data = data;
ptr1->next = *start_ref;
*start_ref = ptr1;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 78, 20, 10, 32, 1, 5 };
int list_size, i;
/* start with empty linked list */
struct Node* start = NULL;
list_size = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
/* Create linked list from the array arr[] */
for (i = 0; i < list_size; i++)
insertAtTheBegin(&start, arr[i]);
/* print list before sorting */
printf("Linked list before sorting\n");
printList(start);
/* sort the linked list */
bubbleSort(&start, list_size);
/* print list after sorting */
printf("Linked list after sorting\n");
printList(start);
return 0;
}
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node* next;
} Node;
struct Node* swap(struct Node* ptr1, struct Node* ptr2)
{
struct Node* tmp = ptr2->next;
ptr2->next = ptr1;
ptr1->next = tmp;
return ptr2;
}
int bubbleSort(struct Node** head, int count)
{
struct Node** h;
int i, j, swapped;
for (i = 0; i < count; i++)
{
h = head;
swapped = 0;
for (j = 0; j < count - i -1; j++)
{
struct Node* p1 = *h;
struct Node* p2 = p1->next;
if (p1->data > p2->data)
{
*h = swap(p1, p2);
swapped = 1;
}
h = &(*h)->next;
}
if (swapped == 0)
break;
}
}
void printList(struct Node* n)
{
while (n != NULL)
{
cout << n->data << " -> ";
n = n->next;
}
cout << endl;
}
void insertAtTheBegin(struct Node** start_ref, int data)
{
struct Node* ptr1
= (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
ptr1->data = data;
ptr1->next = *start_ref;
*start_ref = ptr1;
}
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 8, 2, 4, 1, 5 };
int list_size, i;
struct Node* start = NULL;
list_size = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
for (i = 0; i < list_size; i++)
insertAtTheBegin(&start, arr[i]);
cout <<"Linked list before sorting\n";
printList(start);
bubbleSort(&start, list_size);
cout <<"Linked list after sorting\n";
printList(start);
return 0;
}
//Bubble Sort For Linked List
//By using get higher node
public class LinkedList {
static class Node {
int data;
Node next;
}
public Node head;
//Class constructors
LinkedList() {
head = null;
}
//insert element
public void insert(int value) {
//Create node
Node node = new Node();
node.data = value;
node.next = null;
if (head == null) head = node;
else {
Node temp = head;
//find last node
while (temp.next != null) {
temp = temp.next;
}
temp.next = node;
}
}
//Display all Linked List elements
public void display() {
if (head != null) {
Node temp = head;
while (temp != null) {
System.out.print(" " + temp.data);
temp = temp.next;
}
} else {
System.out.println("Empty Linked list");
}
}
//perform bubble sort in single linked list
public void bubbleSort() {
if (head != null) {
Node current = null,
new_head = null,
move_node = null,
prev = null;
while (head != null) {
prev = null;
current = head;
move_node = head;
while (current != null) {
//When current node value is grator than previous node
if (current.next != null && current.next.data > move_node.data) {
//Swap node values
move_node = current.next;
prev = current;
}
current = current.next;
}
if (move_node == head) {
head = (head).next;
}
if (prev != null) {
prev.next = move_node.next;
}
move_node.next = new_head;
new_head = move_node;
}
//make new head
head = new_head;
} else {
System.out.println("Empty Linked list");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList obj = new LinkedList();
//insert element of linked list
obj.insert(7);
obj.insert(50);
obj.insert(9);
obj.insert(42);
obj.insert(5);
obj.insert(15);
System.out.print("Before sort : ");
//display all node
obj.display();
obj.bubbleSort();
System.out.print("\nAfter sort : ");
obj.display();
}
}
#Bubble Sort For Linked List
#By using get higher node
class Node:
def __init__(self,data):
self.data=data
self.next=None
#Create Class Linked
class Linked:
def __init__(self):
#Assign default value
self.head=None
#insert new node to linked list
def insert(self,data):
node=Node(data)
node.next=None
if self.head==None:
self.head=node
else:
temp=self.head
while temp.next!=None:
temp=temp.next
#add node
temp.next=node
def display(self):
if(self.head==None):
print("Empty Linked List")
return
temp=self.head
while(temp!=None):
print(temp.data,end=" ")
temp=temp.next
#perform bubble sort in single linked list
def bubbleSort(self):
if(self.head!=None):
current=None
new_head=None
move_node=None
prev=None
while(self.head!=None):
prev=None
current=self.head
move_node=self.head
while(current!=None):
#When current node value is grator than previous node
if(current.next!=None and current.next.data>move_node.data):
#Swap node values
move_node=current.next
prev=current
current=current.next
if(move_node==self.head):
self.head=(self.head).next
if(prev!=None):
prev.next=move_node.next
move_node.next=new_head
new_head=move_node
#make new head
self.head=new_head
else:
print("Empty Linked list")
def main():
#Create Object of class Linked
obj=Linked()
#insert element of linked list
obj.insert(7)
obj.insert(50)
obj.insert(9)
obj.insert(42)
obj.insert(5)
obj.insert(15)
print("Before sort : ")
#display all node
obj.display()
obj.bubbleSort()
print("\nAfter sort : ")
obj.display()
if __name__=="__main__":
main()
Output
Linked list before sorting
5 -> 1 -> 4 -> 2 -> 8 ->
Linked list after sorting
1 -> 2 -> 4 -> 5 -> 8 ->
Time Complexity: O(n2), as a nested traversal, is needed.
**Conclusion**
Bubble sort is a simple sorting algorithm that may be used to sort linked lists by exchanging nodes. Although it is not the most efficient approach for huge lists, it might be beneficial in some situations or as a learning exercise. Here are some frequently asked questions about utilising bubble sort in a linked list by exchanging nodes.
## Frequently Asked Questions
**Q1. How does the swapping of nodes work in bubble sort for a linked list?**
In the linked list implementation of bubble sort, swapping nodes involves rearranging the pointers of adjacent nodes to change their positions within the list.
**Q2. What is the time complexity of bubble sort in a linked list?**
The time complexity of bubble sort in a linked list is O(n^2), where “n” represents the number of nodes in the list. This is because each pass through the list requires comparing and potentially swapping adjacent nodes.
**Q3. Is bubble sort efficient for large linked lists?**
No, bubble sort is not efficient for large linked lists. Its quadratic time complexity makes it less suitable for handling large datasets. Other sorting algorithms like to merge sort or quicksort are more efficient choices for larger lists.
**Q4. What are some advantages of using bubble sort in a linked list?**
Bubble sort is relatively easy to implement for linked lists and requires minimal memory usage. It can be useful for educational purposes or for sorting small lists where simplicity is more important than efficiency.
**Q5. Can bubble sort be used for sorting doubly linked lists?**
Yes, bubble sort can be applied to doubly linked lists as well. The swapping of nodes in a doubly linked list involves adjusting the pointers of the adjacent nodes to properly change their positions.


