Last Updated on July 24, 2023 by Mayank Dham

The last node in the linked list is known as the tail node of the linked list. In this article, we will figure out the best way to remove last node from linked list. The removal of the last node is a crucial operation that has implications beyond data management, making it essential to grasp the intricacies and potential pitfalls. As we traverse the landscape of linked list manipulation, we’ll discuss the time and space complexities of each approach, empowering you to make informed decisions when designing solutions for real-world problems.
How to Delete Last Node in Linked List
In this question, we are given a singly linked list. By doing some operations, we have to figure out how to remove last node from linked list.
Suppose, the given linked list is 1 -> 5 -> 9 -> 11 -> 20. Now, we are asked to delete the last node of the given list.
Here, the last node is 20. So, after deleting the last node, the final linked list is 1 -> 5 -> 9 -> 11.
Input:
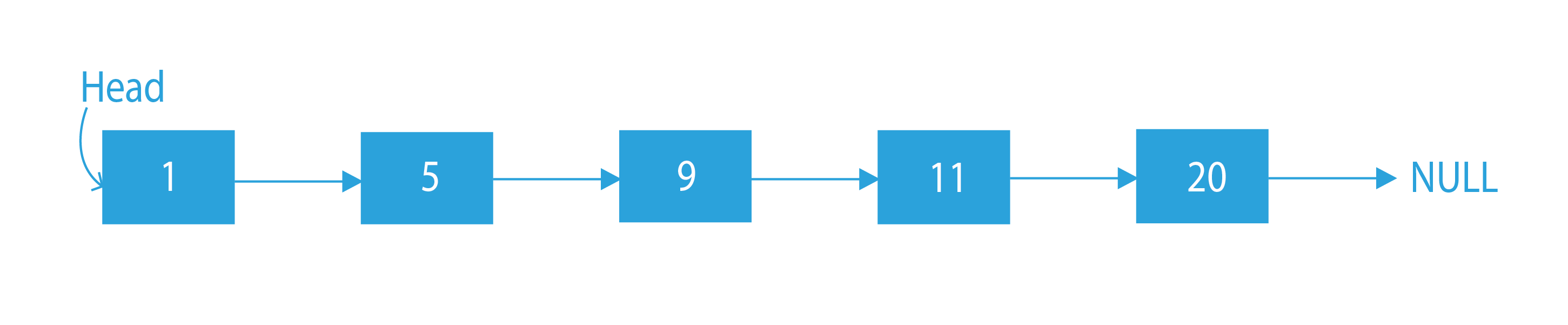
Output:
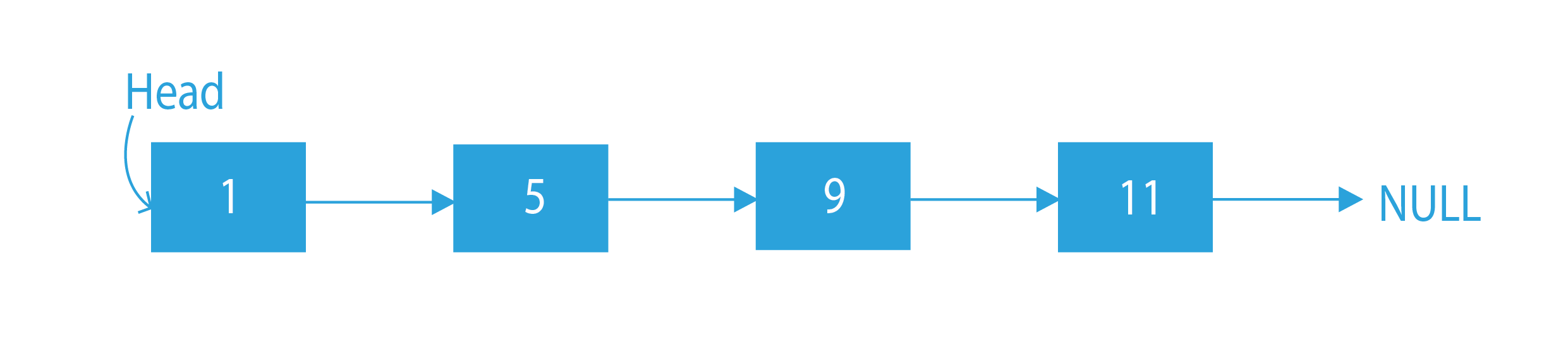
Explanation: As the last node is 20, it is getting removed from the given list.
As we know, insertion and deletion in a singly linked list are very efficient, but list traversal takes O(n) time. We are going to use the list traversal, but with a few tweaks. Let us have a glance at the approach.
Approach to delete last node in linked list
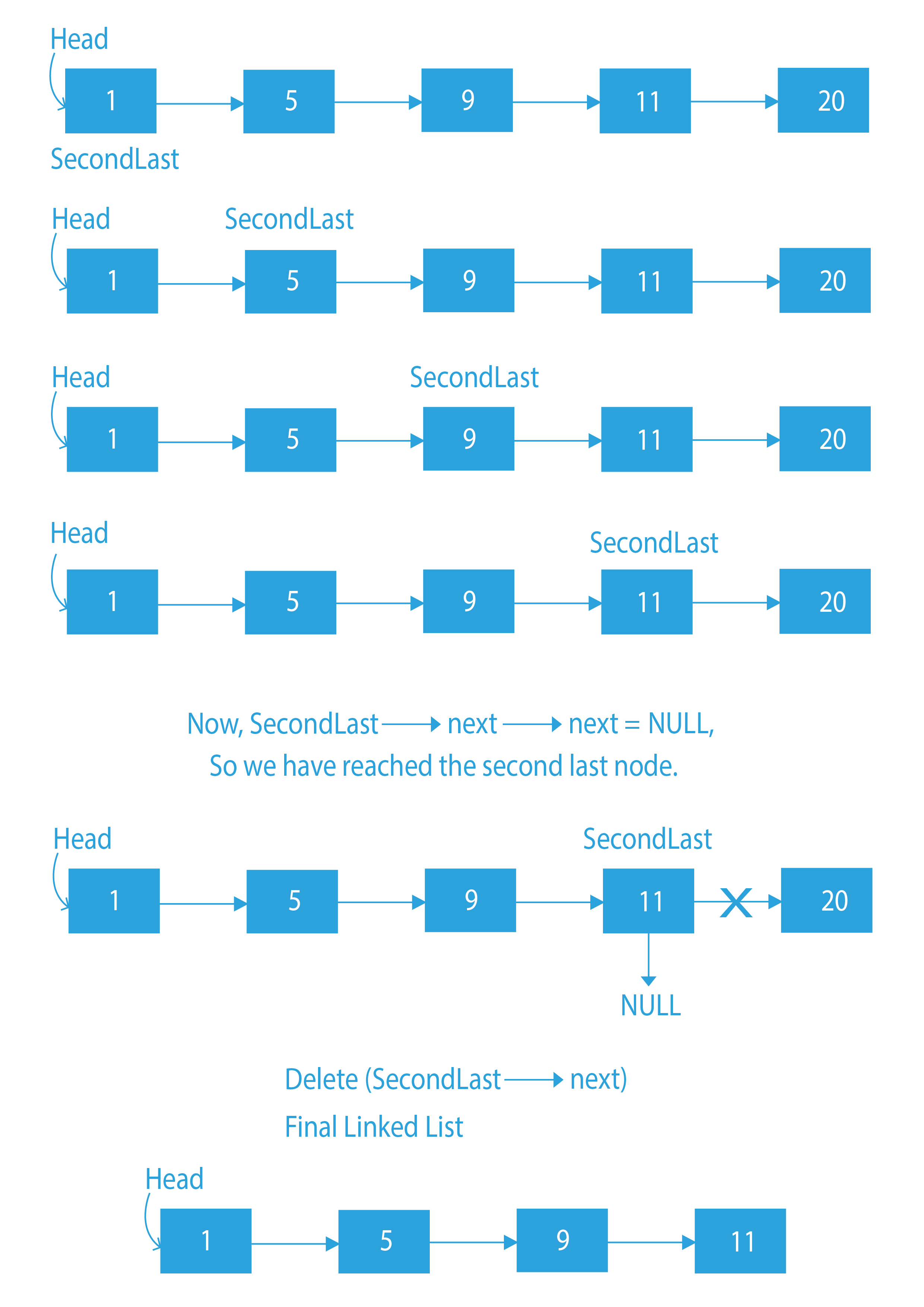
The approach is going to be pretty simple to delete last node in linked list. To remove the last node, what we can do is, reach the second last node, and make it point to NULL. By doing this, we are deleting the last node and making the second last node our new last node.
Algorithm to delete last node in linked list
- Base Case 1 – If the head is NULL, return NULL
- Base Case 2 – if head -> next is NULL, delete the head and return NULL.
- This means that there was only a single node in the linked list.
- Create a new node, say SecondLast and make it point to the head of the list.
- Now, traverse through the list by incrementing SecondLast, till the second last node of the linked list is reached.
- When we reach the second last node of the linked list, simply delete the next of the second last node i.e delete the last node.
- delete(SecondLast -> next).
- Make the second last node point to NULL. This will make our second last node new tail of the list.
- Return head.
Dry Run to delete last node in linked list
Code Implementation to delete last node in linked list
#include <stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node* next;
};
/* Function to remove the last node
of the linked list */
struct Node* removeLastNode(struct Node* head)
{
if (head == NULL)
return NULL;
if (head->next == NULL) {
free(head);
return NULL;
}
// Find the second last node
struct Node* second_last = head;
while (second_last->next->next != NULL)
second_last = second_last->next;
// Delete last node
free(second_last->next);
// Change next of second last
second_last->next = NULL;
return head;
}
// Function to push node at head
void push(struct Node** head_ref, int new_data)
{
struct Node* new_node =
(struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
new_node->data = new_data;
new_node->next = (*head_ref);
(*head_ref) = new_node;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
/* Start with the empty list */
struct Node* head = NULL;
/* Use push() function to construct
the below list 8 -> 23 -> 11 -> 29 -> 12 */
push(&head, 12);
push(&head, 29);
push(&head, 11);
push(&head, 23);
push(&head, 8);
head = removeLastNode(head);
for (struct Node* temp = head; temp != NULL; temp = temp->next)
printf("%d ",temp->data);
return 0;
}
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node* next;
};
Node* removeLastNode(struct Node* head)
{
if (head == NULL)
return NULL;
if (head->next == NULL) {
delete head;
return NULL;
}
Node* second_last = head;
while (second_last->next->next != NULL)
second_last = second_last->next;
delete (second_last->next);
second_last->next = NULL;
return head;
}
void push(struct Node** head_ref, int new_data)
{
struct Node* new_node = new Node;
new_node->data = new_data;
new_node->next = (*head_ref);
(*head_ref) = new_node;
}
int main()
{
Node* head = NULL;
push(&head, 20);
push(&head, 11);
push(&head, 9);
push(&head, 5);
push(&head, 1);
head = removeLastNode(head);
for (Node* temp = head; temp != NULL; temp = temp->next)
cout << temp->data << " ";
return 0;
}
public class PrepBytes {
static class Node {
int data;
Node next;
};
static Node removeLastNode(Node head)
{
if (head == null)
return null;
if (head.next == null) {
return null;
}
Node second_last = head;
while (second_last.next.next != null)
second_last = second_last.next;
second_last.next = null;
return head;
}
static Node push(Node head_ref, int new_data)
{
Node new_node = new Node();
new_node.data = new_data;
new_node.next = (head_ref);
(head_ref) = new_node;
return head_ref;
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
Node head = null;
head = push(head, 20);
head = push(head, 11);
head = push(head, 9);
head = push(head, 5);
head = push(head, 1);
head = removeLastNode(head);
for (Node temp = head; temp != null; temp = temp.next)
System.out.print(temp.data + " ");
}
}
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
def push(head, data):
if not head:
return Node(data)
temp = Node(data)
temp.next = head
head = temp
return head
def removeLastNode(head):
if head == None:
return None
if head.next == None:
head = None
return None
second_last = head
while(second_last.next.next):
second_last = second_last.next
second_last.next = None
return head
if __name__=='__main__':
head = None
head = push(head, 20)
head = push(head, 11)
head = push(head, 9)
head = push(head, 5)
head = push(head, 1)
head = removeLastNode(head)
while(head):
print("{} ".format(head.data), end ="")
head = head.next
Output
1 5 9 11
Space Complexity: O(1), as only temporary variables are bring created.
Conclusion
So, in this article, we have tried to explain the most efficient approach to remove the last node of a linked list. In conclusion, the approach to delete last node in a linked list is a fundamental operation with significant implications for data management and computational efficiency. Throughout this article, we have explored different techniques and algorithms to expertly remove the last node in a linked list, catering to both singly and doubly linked structures. We began by revisiting the basics of linked lists and their implementation, laying a strong foundation for a deeper understanding of node deletion.
FAQs on how to delete last node in linked list.
Q: Can I use the iterative method to delete the last node in a singly or doubly linked list?
A: Yes, the iterative approach is applicable to both singly and doubly linked lists. In a singly linked list, you can traverse to the second-to-last node using two pointers, while in a doubly linked list, you can directly delete the last node.
Q: How does the recursive method work in deleting the last node?
A: The recursive method uses a recursive function to traverse the linked list until the last node is reached. Once the last node is identified, it is deleted from the list. The recursion continues until the entire list is traversed.
Q: What is the time complexity of deleting the last node using the iterative method?
A: The time complexity is O(n), where n is the number of nodes in the linked list. Since the iterative method traverses the entire list to find the last node, the time taken is directly proportional to the size of the list.
Q: Can I use the recursive method to delete the last node in a circular linked list?
A: Yes, the recursive method can be adapted to work with circular linked lists as well. The recursive function needs to handle the case when the next node is the first node, indicating that it has reached the end of the circular list.
Q: How can I avoid errors when deleting the last node in an empty linked list?
A: It is essential to include error handling in your code to account for edge cases, such as attempting to delete the last node in an empty linked list. Before performing any deletion operation, ensure that the list is not empty to prevent errors and unexpected behavior.


