Last Updated on July 24, 2023 by Mayank Dham

In certain situations, linked lists are preferred over arrays because they offer faster insertion and deletion operations. Unlike arrays, linked lists do not require a predefined size. As a result, we will explore how to convert array to linked list in this blog. Let’s examine the problem statement to gain a clearer understanding.
How to convert array to linked list
In this particular problem, we are presented with an array and tasked with constructing a linked list based on the given array. The concept behind this task is straightforward, making it a fundamental exercise for grasping the fundamentals of linked lists.
Let me explain this problem with an example test case-
Sample Input
Array: arr[]={0, 2, 3, 5, 1}
Sample Output
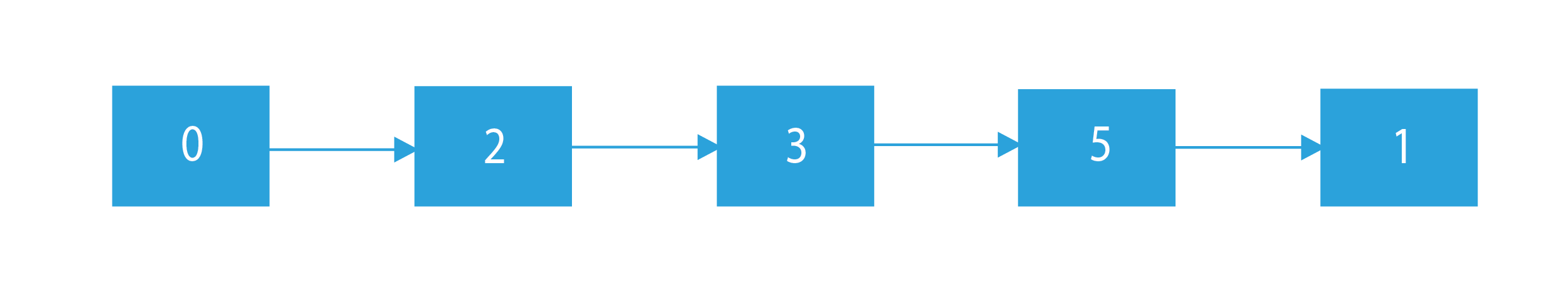
Approach regarding create linked list from a given array
The approach involves traversing the array from one end to the other. For each element encountered during the traversal, a new node is created with that element’s value, and then the node is inserted into the linked list.
Algorithm to convert array to linked list
Algorithm to convert array to linked list
- Here’s a step-by-step algorithm to convert array to linked list:
- Start with an empty linked list (initialize the head pointer as null).
- Traverse the array from the beginning to the end.
- For each element in the array:
- Create a new node with the current element’s value.
- If the linked list is empty (head is null), set the new node as the head.
- Otherwise, set the next pointer of the last node in the linked list to point to the new node.
- Update the last node pointer to the newly created node.
- After processing all elements in the array, the linked list is constructed.
Dry Run on How to convert array to linked list
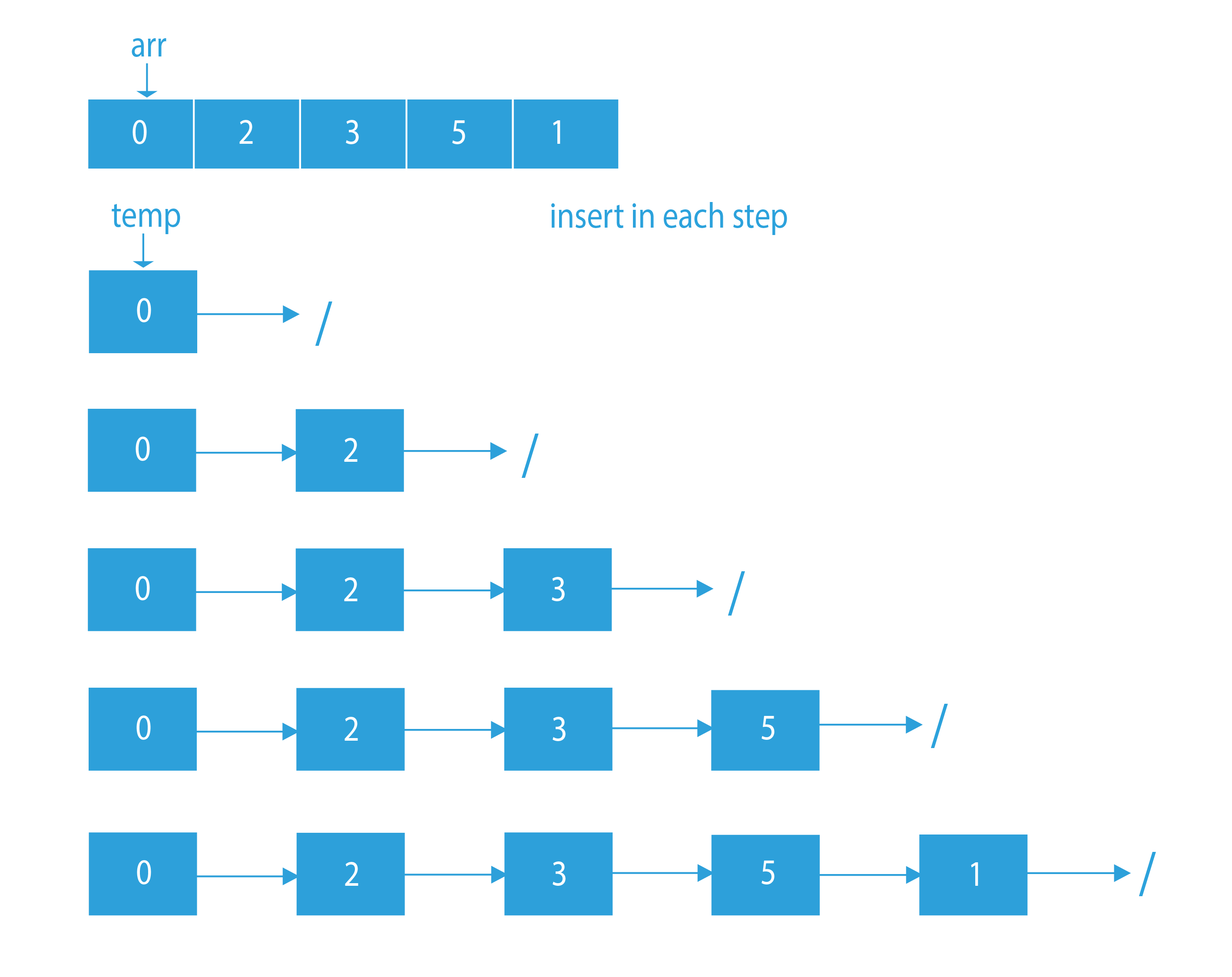
Code Implementation to create linked list from array
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node* next;
};
void insert(struct Node** root, int item)
{
struct Node* temp = (struct Node*) malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
struct Node* ptr;
temp->data = item;
temp->next = NULL;
if (*root == NULL)
*root = temp;
else {
ptr = *root;
while (ptr->next != NULL)
ptr = ptr->next;
ptr->next = temp;
}
}
void print(struct Node* root)
{
while (root != NULL) {
printf("%d->", root->data);
root = root->next;
}
}
struct Node *arrayToList(int arr[], int n)
{
struct Node *root = NULL;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
insert(&root, arr[i]);
return root;
}
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 0, 2, 3, 5, 1 };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
struct Node* root = arrayToList(arr, n);
print(root);
return 0;
}
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct Node {
int data;
Node* next;
};
void insert(Node** root, int item)
{
Node* temp = new Node;
Node* ptr;
temp->data = item;
temp->next = NULL;
if (*root == NULL)
*root = temp;
else {
ptr = *root;
while (ptr->next != NULL)
ptr = ptr->next;
ptr->next = temp;
}
}
void print(Node* root)
{
while (root != NULL) {
cout << root->data << " ";
root = root->next;
}
}
Node *arrayToList(int arr[], int n)
{
Node *root = NULL;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
insert(&root, arr[i]);
return root;
}
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 0, 2, 3, 5, 1 };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
Node* root = arrayToList(arr, n);
print(root);
return 0;
}
class LinkedList
{
// Representation of a node
static class Node
{
int data;
Node next;
};
static Node root;
// Function to insert node
static Node insert(Node root, int item)
{
Node temp = new Node();
temp.data = item;
temp.next = root;
root = temp;
return root;
}
static void display(Node root)
{
while (root != null)
{
System.out.print(root.data + " ");
root = root.next;
}
}
static Node arrayToList(int arr[], int n)
{
root = null;
for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0 ; i--)
root = insert(root, arr[i]);
return root;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int arr[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
int n = arr.length;
Node root = arrayToList(arr, n);
display(root);
}
}
class Node: def __init__(self, data): self.data = data self.next = None def insert(root, item): temp = Node(item) if (root == None): root = temp else : ptr = root while (ptr.next != None): ptr = ptr.next ptr.next = temp return root def display(root): while (root != None) : print(root.data, end = " ") root = root.next def arrayToList(arr, n): root = None for i in range(0, n, 1): root = insert(root, arr[i]) return root if __name__=='__main__': arr = [0, 2, 3, 4, 5, 1] n = len(arr) root = arrayToList(arr, n) display(root)
Output:
0->2->3->5->1
Space complexity to create linked list from array : O(1), no extra space is used in this approach.
Conclusion
This blog tried to discuss how easily you can create linked list from array and described their time and space complexities. Also, we will explain the proper step-by-step dry run for better understanding. Hope this article “create linked list from array ” enhances your knowledge of linked lists. To practice more problems on LinkedList you can check out at PrepBytes Linked List.
Conclusion
Converting an array to a linked list is a fundamental operation in data structure and programming. The process involves traversing the array and creating a new node for each element, which is then inserted into the linked list. This conversion is valuable when dealing with dynamic data structures, as linked lists offer more flexibility in memory allocation and faster insertion and deletion operations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) related to converting array to linked list:
Q1. Why would you convert an array to a linked list?
Converting an array to a linked list is beneficial when you need to handle dynamic data or perform frequent insertions or deletions. Linked lists offer better performance for these operations compared to arrays, which require resizing and shifting elements for dynamic changes.
Q2. What is the time complexity of converting an array to a linked list?
The time complexity of converting an array to a linked list is O(n), where n is the number of elements in the array. This is because you need to traverse the entire array to create nodes for each element.
Q3. Can you convert a linked list back to an array?
Yes, it is possible to convert a linked list back to an array. You would need to traverse the linked list and store each element’s value in an array. The time complexity for this conversion is also O(n), where n is the number of elements in the linked list.
Q4. When should I use an array instead of a linked list?
Arrays are generally more efficient for random access and have better cache locality, making them suitable for scenarios where you frequently need to access elements by their index. Linked lists are more appropriate for situations requiring frequent insertions and deletions, especially in the middle of the data structure.
Q5. Are there any limitations to using linked lists?
Linked lists have some drawbacks, such as the additional memory overhead for maintaining node references and the lack of constant-time random access. Additionally, traversing a linked list to find a specific element may take longer than using an array with direct access.
Q6. Can I convert a multidimensional array to a linked list of linked lists?
Yes, you can convert a multidimensional array to a linked list of linked lists by recursively converting each dimension into a separate linked list. Each node in the outer linked list would point to another linked list representing the inner dimension.


