Last Updated on July 27, 2023 by Mayank Dham

Linked lists are essential data structures used in computer programming to efficiently store and manage collections of elements. Inserting a new node before a specified position in a singly linked list is a common operation that allows programmers to dynamically expand and modify the list as needed.
In this article, we will delve into the process of inserting a node before a specified position in a singly linked list using C programming language. We will explore the fundamentals of singly linked lists, understanding the node structure and the connections that form the list. By providing step-by-step explanations and practical examples, readers will gain a comprehensive understanding of how to implement the insert operation effectively. Here we will learn in detail how to insert a node at a specific position in a linked list in C.
How to Insert a Node at a Specific Position in a Linked List in C?
The problem is quite simple. We just have to insert a node at a specific position in a linked list in C. Here is an example to understand what is meant by to insert a node at a specific position in a linked list.
Example :
Input:
list = 1→2→3→4→5,
data = 6
position = 2Output:
1 → 6 → 2→ 3 → 4 → 5Explanation:
Suppose the given list is 1 → 2 → 3 → 4 → 5, position = 2, and the data to be inserted is 6.
- According to the problem statement, we need to insert a node with value = 6 at 2nd position in the linked list.
- So, after adding the node with value = 6 at the 2nd position in the given linked list, our resultant list will be 1 → 6 → 2→ 3 → 4 → 5.
Now the problem statement is clear. So, now the main question is how we should approach this problem. What is the first thing that comes to mind when we talk about insertion at a specific position in a linked list?
- List traversal, right? Yes. We are going to use list traversal for insertion at a specific position in a linked list.
Before moving further to the approach section, try to think of the approach by yourself.
- If stuck, no problem, we will thoroughly see how we can approach this problem in the next section.
Let’s move to the approach section.
Approach to Insert a Node at a Specific Position in a Linked List in C
Our approach to insert at any position in linked list is going to be pretty simple. Here is our approach.
- We will simply traverse till (position -1)th node and add the newnode just after that node. Well, how will this work? Let us take an example.
- Suppose the list is 1 → 2 → 3, and we have to insert 4 at the 2nd position.
- Now, we will traverse (position -1) = (2-1) = 1 node and after traversing 1 node, we will be standing at 1.
- Now we will make 4 → next = 1 → next as we have to insert it after 1, and finally, 1 → next = 4 to link the nodes.
- By doing the above steps, 4 will be added at that specific position, and our resultant linked list will be: 1 → 4 → 2 → 3.
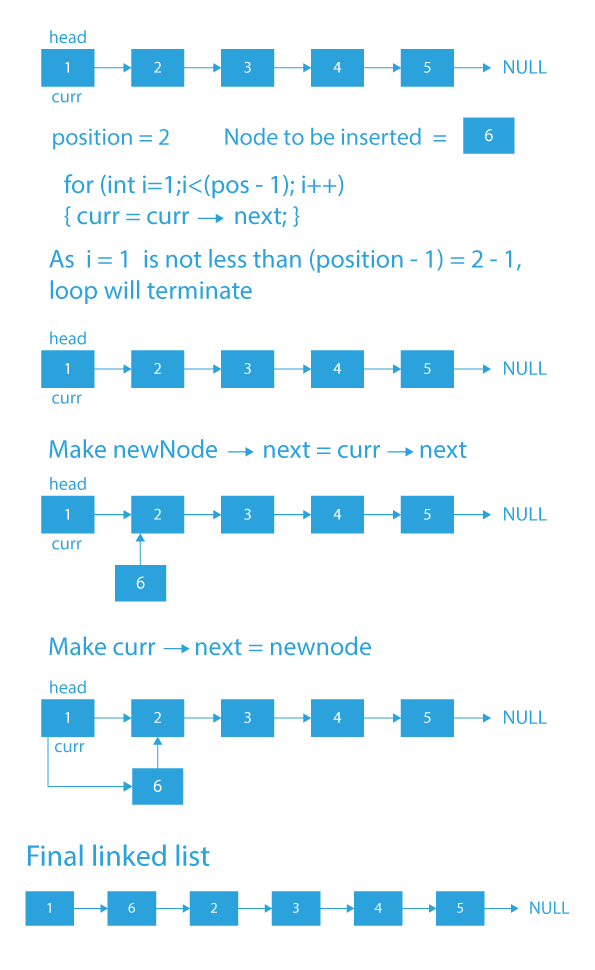
We can get a clearer look at the approach by looking at the dry run.
Algorithm to Insert a Node at a Specific Position in a Linked List in C
The algorithm to insert a node at a specific position in a linked list is given below.
- If the position where we are asked to insert pos is smaller than 1 or greater than the size of the list, it is invalid, and we will return.
- Else, we will make a variable curr and make it point to the head of the list.
- Now we will run a for loop using curr to reach to the node at (pos-1)th position:
- The for loop will be: for(int i=1;inext;}
- After the termination of the above loop, curr will be standing at the (position – 1)th node.
- As explained above, we will simply make newnode → next = curr → next and curr → next = newnode.
- If the pos was equal to 1, we will make the head point to newnode as newnode will become the first node of the list.
Dry Run to Insert a Node at a Specific Position in a Linked List in C
Now, it is the showdown. Let’s see the code implementation to insert a node from linked list at a given position in C, C++, Java and in Python.
Code to Insert a Node at a Specific Position in a Linked List in C
Here is the code implementation for how to insert a node at a specific position in a linked list in C, C++, Java, and Python.
n.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node* next;
};
int size = 0;
// Using this function we will be creating new nodes
struct Node* getNode(int data)
{
struct Node* newNode
= (struct Node*)malloc(
sizeof(struct Node));
newNode->data = data;
newNode->next = NULL;
return newNode;
}
// Using this function we will insert the newnode at the specific position
void insertAtPosition(struct Node* head, int pos, int data)
{
if (pos < 1 || pos > size + 1)
printf( "Invalid position!\n" );
else {
struct Node *curr=head;
for(int i=1;i<pos-1;i++) curr="curr-">next;
struct Node* temp=getNode(data);
temp->next=curr->next;
curr->next=temp;
if(pos=1)
head=temp;
size++;
}
}
// Using this function we will print the linked list
void printList(struct Node* head)
{
while (head != NULL) {
printf("%d ",head->data);
head = head->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
// Driver function
int main()
{
struct Node* head = NULL;
head = getNode(1);
head->next = getNode(2);
head->next->next = getNode(3);
head->next->next->next = getNode(4);
head->next->next->next->next = getNode(5);
size = 5;
printf("Linked list before insertion: ");
printList(head);
int data = 6, pos = 2;
insertAtPosition(head, pos, data);
printf("Linked list after insertion of 6 at position 2: ");
printList(head);
return 0;
}
#include <bits stdc++.h="">
using namespace std;
// Node structure of a singly linked list node
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node* next;
};
int size = 0;
// Using this function we will be creating new nodes
Node* getNode(int data)
{
Node* newNode = new Node();
newNode->data = data;
newNode->next = NULL;
return newNode;
}
// Using this function we will insert the newnode at the specific position
void insertAtPosition(Node* head, int pos, int data)
{
if (pos < 1 || pos > size + 1)
cout << "Invalid position!" << endl;
else {
Node *curr=head;
for(int i=1;i<pos-1;i++) {="" curr="curr-">next;
}
Node* temp=getNode(data);
temp->next=curr->next;
curr->next=temp;
if(pos=1)
head=temp;
size++;
}
}
// Using this function we will print the linked list
void printList(struct Node* head)
{
while (head != NULL) {
cout << " " << head->data;
head = head->next;
}
cout << endl;
}
// Driver function
int main()
{
Node* head = NULL;
head = getNode(1);
head->next = getNode(2);
head->next->next = getNode(3);
head->next->next->next = getNode(4);
head->next->next->next->next = getNode(5);
size = 5;
cout << "Linked list before insertion: ";
printList(head);
int data = 6, pos = 2;
insertAtPosition(head, pos, data);
cout << "Linked list after insertion of 6 at position 2: ";
printList(head);
return 0;
}
public class PrepBytes {
// Structure of a singly linked list node
static class Node {
public int data;
public Node nextNode;
public Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
}
// Function to create a new node and return
static Node GetNode(int data) {
return new Node(data);
}
// Function to insert an element at a specified index
static Node InsertAtPos(Node headNode, int position, int data) {
Node head = headNode;
if (position < 1)
System.out.print("Invalid position");
if (position == 1) {
Node newNode = new Node(data);
newNode.nextNode = headNode;
head = newNode;
} else {
for(int i=1;i<position - 1;i++)
{
headNode=headNode.nextNode;
}
Node newNode= new Node(data);
newNode.nextNode=headNode.nextNode;
headNode.nextNode=newNode;
}
return head;
}
// Function to print the list
static void PrintList(Node node) {
while (node != null) {
System.out.print(node.data);
node = node.nextNode;
if (node != null)
System.out.print(",");
}
System.out.println();
}
// Driver function
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node head = GetNode(1);
head.nextNode = GetNode(2);
head.nextNode.nextNode = GetNode(3);
head.nextNode.nextNode.nextNode = GetNode(4);
head.nextNode.nextNode.nextNode.nextNode = GetNode(5);
System.out.print("Linked list before insertion: ");
PrintList(head);
int data = 6, pos = 2;
head = InsertAtPos(head, pos, data);
System.out.print("Linked list after" + " insertion of 6 at position 2: ");
PrintList(head);
}
}
# A linked list Node
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.nextNode = None
# function to create and return a Node
def getNode(data):
newNode = Node(data)
return newNode
# function to insert a Node at required position
def insertPos(headNode, position, data):
head = headNode
if (position < 1):
print("Invalid position!")
if position == 1:
newNode = Node(data)
newNode.nextNode = headNode
head = newNode
else:
while (position != 0):
position -= 1
if (position == 1):
newNode = getNode(data)
newNode.nextNode = headNode.nextNode
headNode.nextNode = newNode
break
headNode = headNode.nextNode
if headNode == None:
break
if position != 1:
print("position out of range")
return head
def printList(head):
while (head != None):
print(' ' + str(head.data), end = '')
head = head.nextNode
print()
if __name__=='__main__':
head = getNode(1)
head.nextNode = getNode(2)
head.nextNode.nextNode = getNode(3)
head.nextNode.nextNode.nextNode = getNode(4)
head.nextNode.nextNode.nextNode.nextNode = getNode(5)
print("Linked list before insertion: ", end='')
printList(head)
data = 6
position = 2
head = insertPos(head, position, data)
print("Linked list after insertion of 6 at position 2: ", end = '')
printList(head)
Output:
Linked list before insertion: 1,2,3,4,5
Linked list after insertion of 6 at position 2: 1,6,2,3,4,5Time Complexity: O(n) is the time complexity to insert a node before specified position in singly linked list in C programming, as we are traversing the whole linked list to reach the desired position.
Space Complexity: O(1) is the space complexity to insert a node before specified position in singly linked list in C programming, since we have not used any extra space for inserting a single node in the linked list.
Conclusion
In conclusion, inserting a node before a specified position in a singly linked list using C offers a powerful way to dynamically expand and modify the list’s content. Throughout this article, we explored the intricacies of singly linked lists, understanding the node structure and the connections that form the list. By providing step-by-step explanations and practical examples, readers gained a comprehensive understanding of how to efficiently implement the insert operation.
We learned that the insert operation involves traversing the linked list to find the target position, creating a new node, and updating pointers to seamlessly integrate the new node into the list. We also discussed essential memory management considerations to prevent memory leaks and ensure efficient memory allocation during the insert operation.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on insert a node before specified position in singly linked list in C
Here are some Frequently Asked Questions on how to insert a node at a specific position in a linked list in C.
1. Can I insert a node at the beginning (head) of the singly linked list?
Yes, to insert a node at the head, simply update the head pointer to point to the new node, and set the new node’s next pointer to the current head.
2. What happens if the specified position is beyond the list’s length?
If the specified position is beyond the list’s length, the new node will be inserted at the end of the list.
3. How does the time complexity of the insert operation in a singly linked list compare to an array?
The time complexity of the insert operation in a singly linked list is O(n), where n is the position of insertion. In an array, it is O(n) as well, but it may require shifting elements after the insertion point, resulting in a potential O(n) for worst-case scenarios.
4. Can I insert multiple nodes before the same specified position?
Yes, you can insert multiple nodes before the same position by repeating the insert operation with different data.
5. What is the role of a temporary pointer in the insert operation?
The temporary pointer is used to traverse the linked list to find the specified position for the new node’s insertion.
6. Is it possible to insert a node before the first occurrence of a specific value in the linked list?
Yes, you can find the first occurrence of the specific value while traversing the list and then perform the insert operation before that position.
7. Can I insert a node before a specified position in a doubly linked list using similar steps?
Yes, the process of inserting a node before a specified position in a doubly linked list is similar, but it requires updating both the previous and next pointers of the nodes involved.


