Last Updated on May 11, 2023 by Prepbytes

An abstract data structure is called a linked list and is made up of an ordered series of nodes. Each node includes data and details about the node after it in the chain of nodes. The linked list can be used to generate a variety of algorithmic challenges. Reversing a linked list while it is in use is one of these issues. By switching the orientation between each link, this issue can be resolved iteratively or recursively.
How To Reverse A Linked List In Python?
Let’s understand the problem statement first to reverse a linked list in Python. The challenge is to reverse a linked list in situ given its head pointer. This indicates that neither shuffling the data field nor using auxiliary space to build a new linked list is permitted. In Python, this issue is frequently referred to as linked list reverse.
Example
Suppose the nodes of the linked list are numbered and links are represented using arrows. So if we are given the head pointer to the linked list: 1 → 2 → 3 → 4 → 5 Then our algorithm should provide a linked list reverse in Python as 5 → 4 → 3 → 2 → 1 The new head pointer should be at node 5.

Algorithm
The basic idea of the problem is to traverse the linked list and reverse the links between nodes one at a time. For example, suppose we start with: 1 → 2 → 3 → 4 → 5 First, we will reverse the link between node 1 and node 2. 1 ← 2 Next, we will reverse the link between node 2 and node 3. 1 ← 2 ← 3 We will repeat the process until we reverse all the links to get: 1 ← 2 ← 3 ← 4 ← 5
We will discuss two different approaches for writing a python program to reverse a linked list below.
Approach1 (Iterative) to Reverse a Linked List in Python
The approach is going to be pretty simple:
- Create two nodes, say, prev and curr.
- prev will initially point to None and the curr will point to the head of the list.
- Now, we have to traverse through the list till the curr becomes None.
- For every node, we are going to store the next of curr in next and then will make the next of current point to prev. Finally we will make prev equal to curr, and curr equal to next.
By performing the above operations, we are changing the links of every node and ultimately reversing the list.
Algorithm1 (Iterative) to Reverse a Linked List in Python
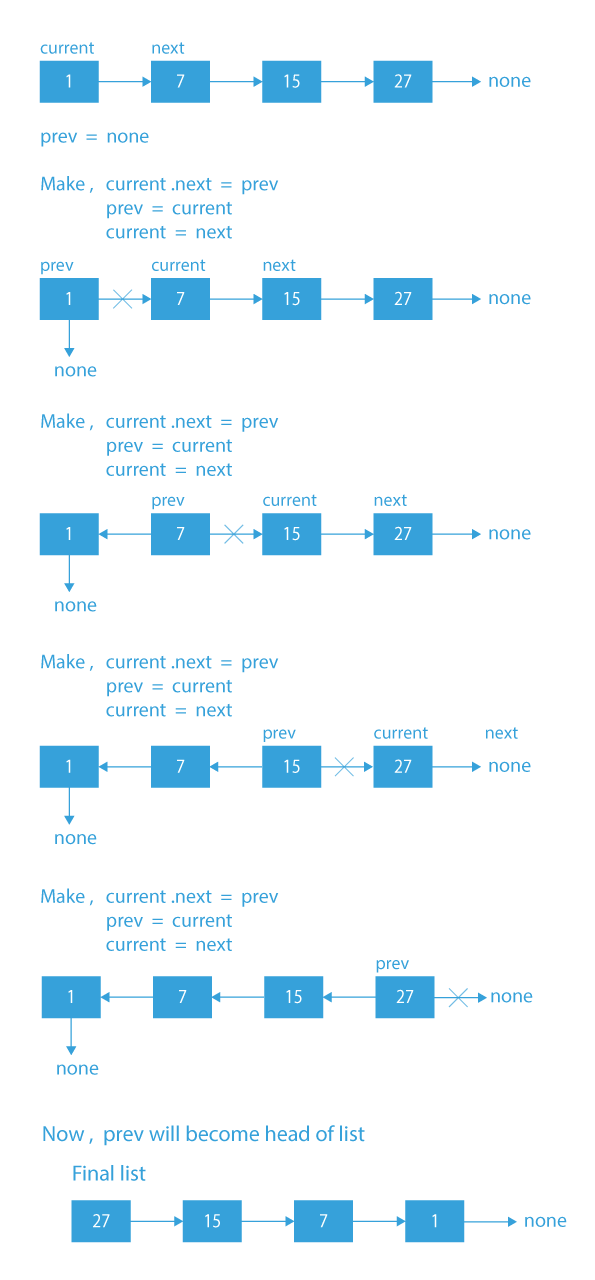
- Create two nodes – prev and current, prev will point to None and curr will point the head.
- Traverse through the list till curr becomes None.
- Store the next of curr in next.
- Now, make the next of curr point to prev.
- After pointing to prev, we will make the prev equal to the curr, and curr equal to the next.
- In the end, after the full traversal, the prev will be our head (head = prev).
Dry Run for the Iterative Approach to Reverse a Linked List in Python
Code Implementation
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
class LinkedList:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
def reverse(self):
prev = None
current = self.head
while(current is not None):
next = current.next
current.next = prev
prev = current
current = next
self.head = prev
def push(self, new_data):
new_node = Node(new_data)
new_node.next = self.head
self.head = new_node
def printList(self):
temp = self.head
while(temp):
print (temp.data)
temp = temp.next
llist = LinkedList()
llist.push(27)
llist.push(15)
llist.push(7)
llist.push(1)
print ("Given Linked List \n")
llist.printList()
llist.reverse()
print ("\nReversed Linked List")
llist.printList()
Output
Given Linked List
1 7 15 27
Reversed Linked List
27 15 7 1Time Complexity – O(n), as list traversal is needed.
Space Complexity – O(1), as only temporary variables are being created.
Approach (Recursive) to Reverse a Linked List in Python
The recursive approach is going to be very much similar to the iterative approach.
- If the current node is the last node, then we will mark it as our head, and it will now point to the prev node.
- If the base case fails, we will store the next of current in next, and make the current point to the previous node. After doing this, we will recur with next as current, and current as previous.
By performing the above operations, we are changing the links of every node and ultimately reversing the list.
Algorithm to Reverse a Linked List in Python
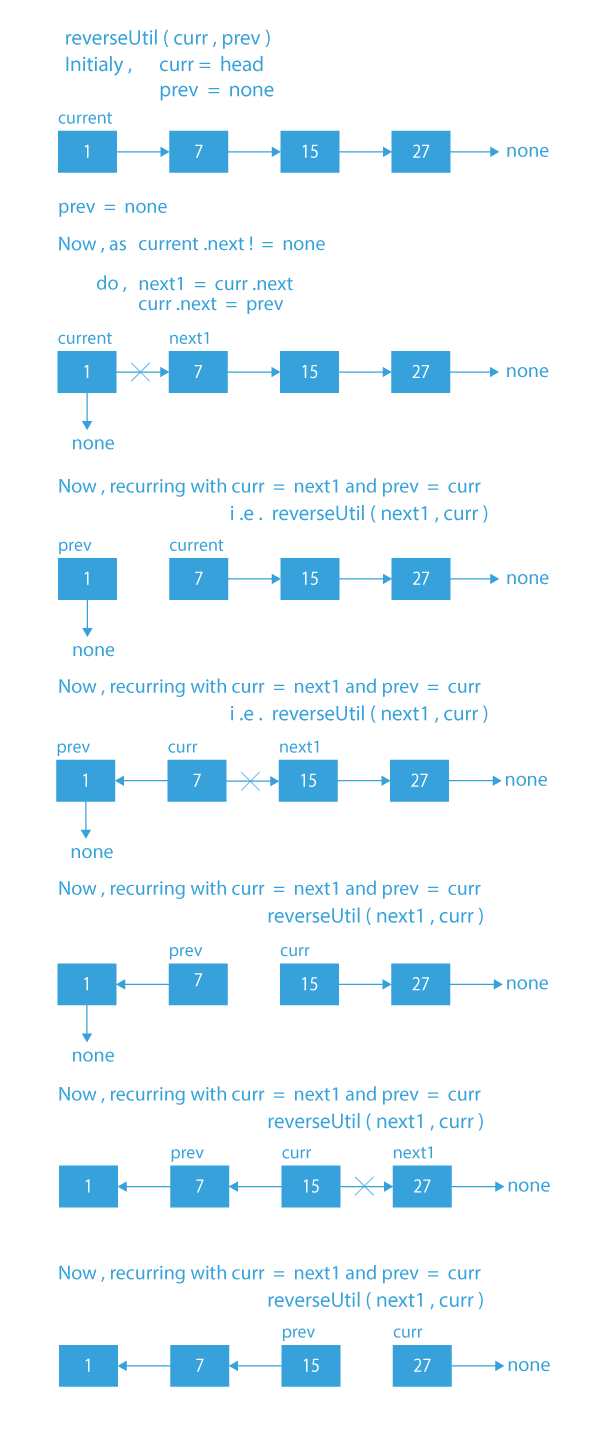
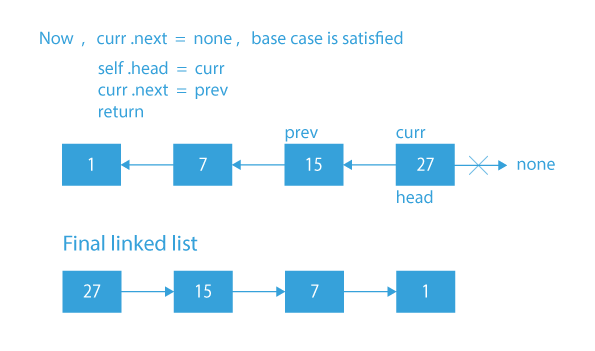
- Base case – If the curr node is the last node, make it the head and also make next of curr point to the prev.
- Save the next of curr in next.
- Now, make the next of curr point to the prev.
- Recur with next as curr and curr as prev.
- Finally, return the head.
Dry Run for the Recursive Approach to Reverse a Linked List in Python
Code Implementation
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
class LinkedList:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
def reverseUtil(self, curr, prev):
if curr.next is None:
self.head = curr
curr.next = prev
return
next = curr.next
curr.next = prev
self.reverseUtil(next, curr)
def reverse(self):
if self.head is None:
return
self.reverseUtil(self.head, None)
def push(self, new_data):
new_node = Node(new_data)
new_node.next = self.head
self.head = new_node
def printList(self):
temp = self.head
while(temp):
print (temp.data),
temp = temp.next
llist = LinkedList()
llist.push(27)
llist.push(15)
llist.push(7)
llist.push(1)
print ("Given linked list\n")
llist.printList()
llist.reverse()
print ("\nReverse linked list")
llist.printList()
Output
Given Linked List
1 7 15 27
Reversed Linked List
27 15 7 1Time Complexity – O(n), as list traversal is needed.
Conclusion
We had discussed two different approaches i.e. iterative and recursive to implement a Python program to reverse a linked list. There are more ways to reverse a linked list in Python. By practicing more about data structures anyone can figure out
FAQ Related to Reverse a Linked List In Python
Q1. From a placement perspective, reverse a linked list in Python is important?
Ans. The answer is “YES”, Python program to reverse a linked list is asked in many organizations for SDE roles i.e. Capgemini, Wipro, TCS, Accenture, Cognizant, and many more.
Q2. Is there any inbuilt function to reverse a linked list in Python?
Ans. No, There is no inbuilt function to reverse a linked list in Python, the user has to define and create its own function to reverse a linked list in Python.
Q3. What are the 4 types of linked lists?
Ans. There are four key types of linked lists:
- Singly-linked lists.
- Doubly linked lists.
- Circular linked lists.
- Circular doubly linked lists.
Other Python Programs
Python program to reverse a number
Python program for heap sort
Python program to check armstrong number
Python program to check leap year
Python program to convert celsius to fahrenheit
Python program to find factorial of a number
Python program to find the middle of a linked list using only one traversal
Python program to add two numbers


