Last Updated on July 27, 2023 by Mayank Dham

We will examine how to program a menu-driven program in C that performs all operations on a doubly linked list in the article below. Usually, a doubly linked list consists of three main parts: the data section, the reference to the next node, and the reference to the previous node.
Operations of Doubly Linked List in C
- traverse(): traverse() function traverses the linked list and prints the node’s data of the doubly linked list.
- insertAtFront(): function to insert an element at the front of the doubly linked list.
- insertAtEnd(): function to insert an element at the end of the doubly linked list.
- insertAtPosition(): function to insert an element at a given position in the doubly linked list.
- deleteFirst(): function to delete an element from the front of the doubly linked list.
- deleteEnd(): function to delete an element from the end of the doubly linked list.
- deletePosition(): function to delete an element from a given position in the doubly linked list.
Dry Run of the Operations of Doubly Linked List
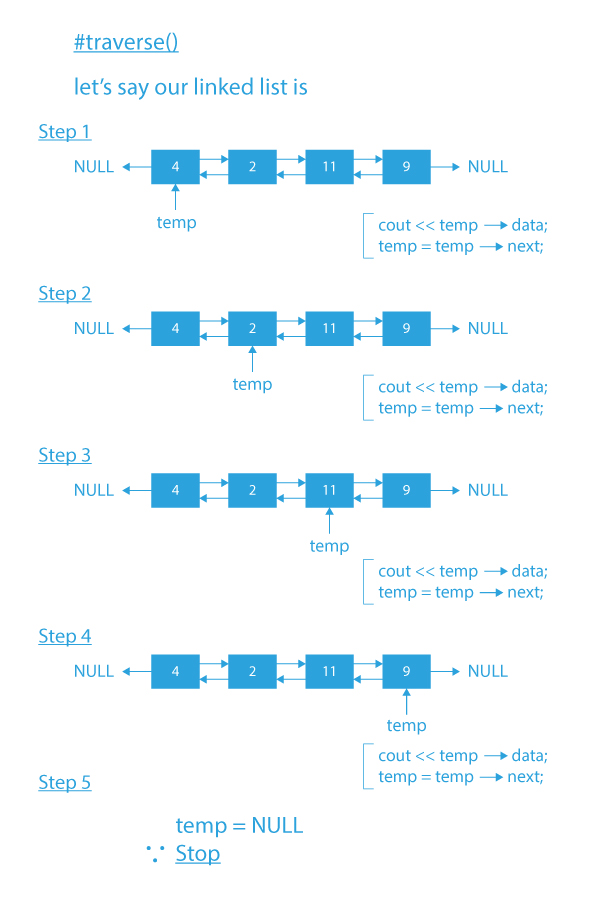
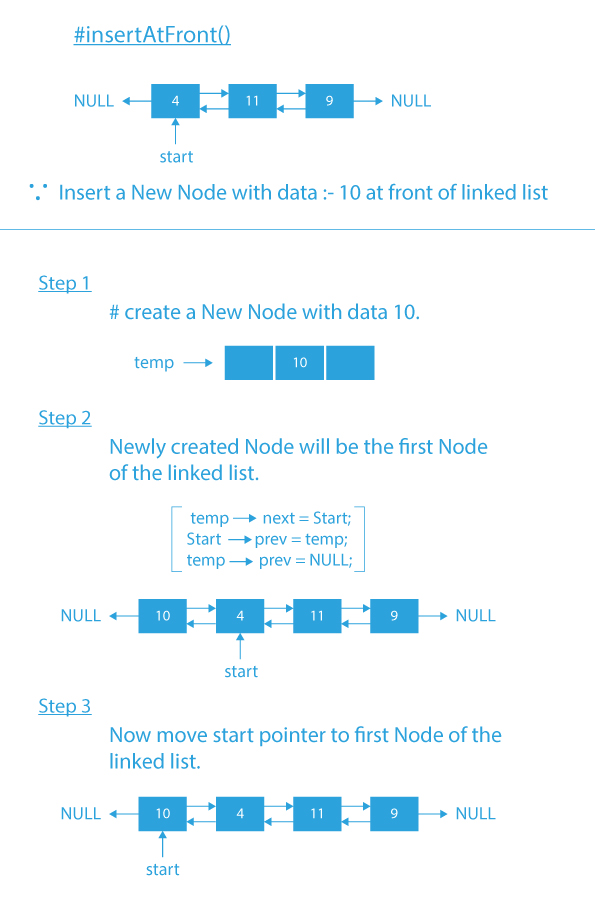
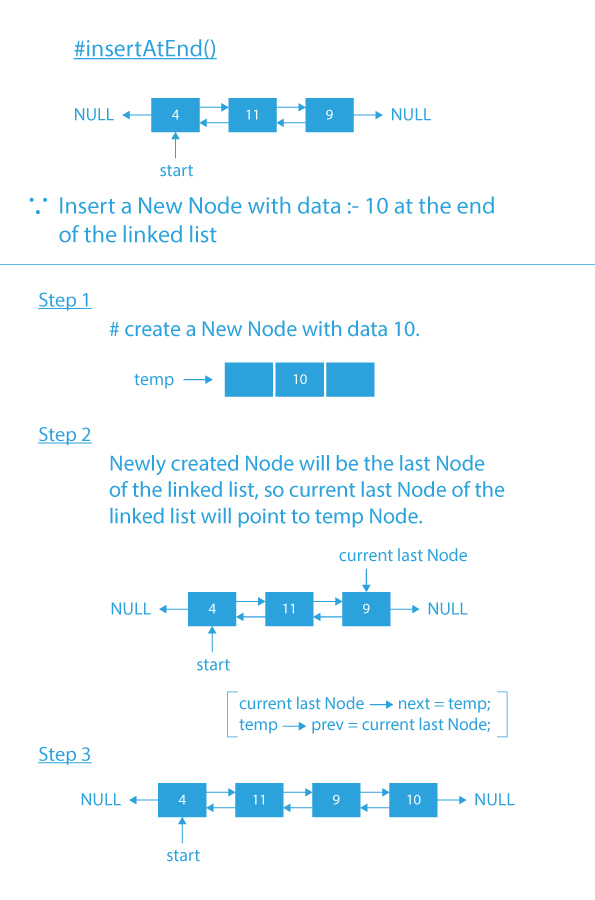
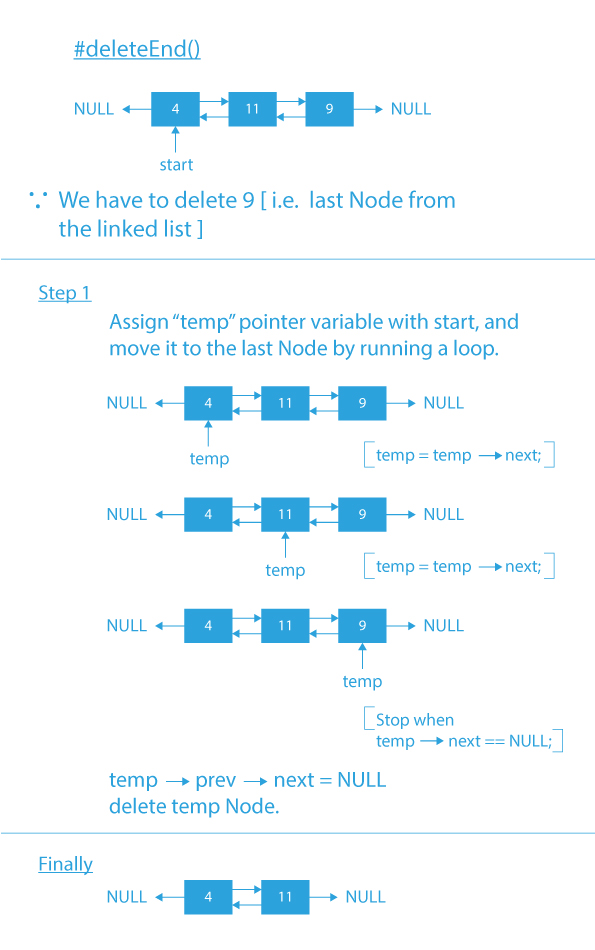
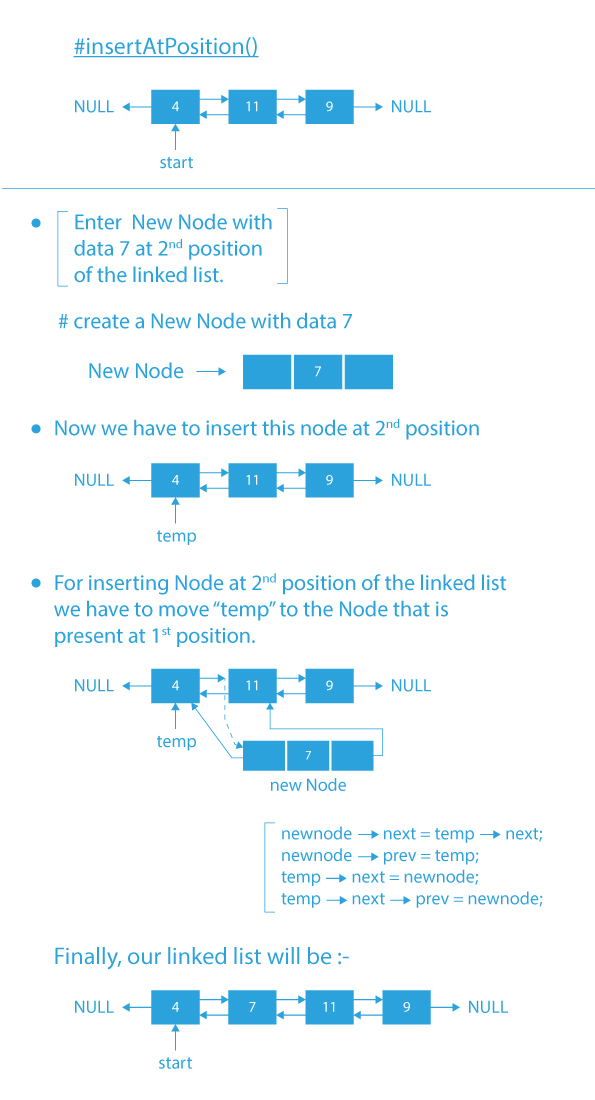
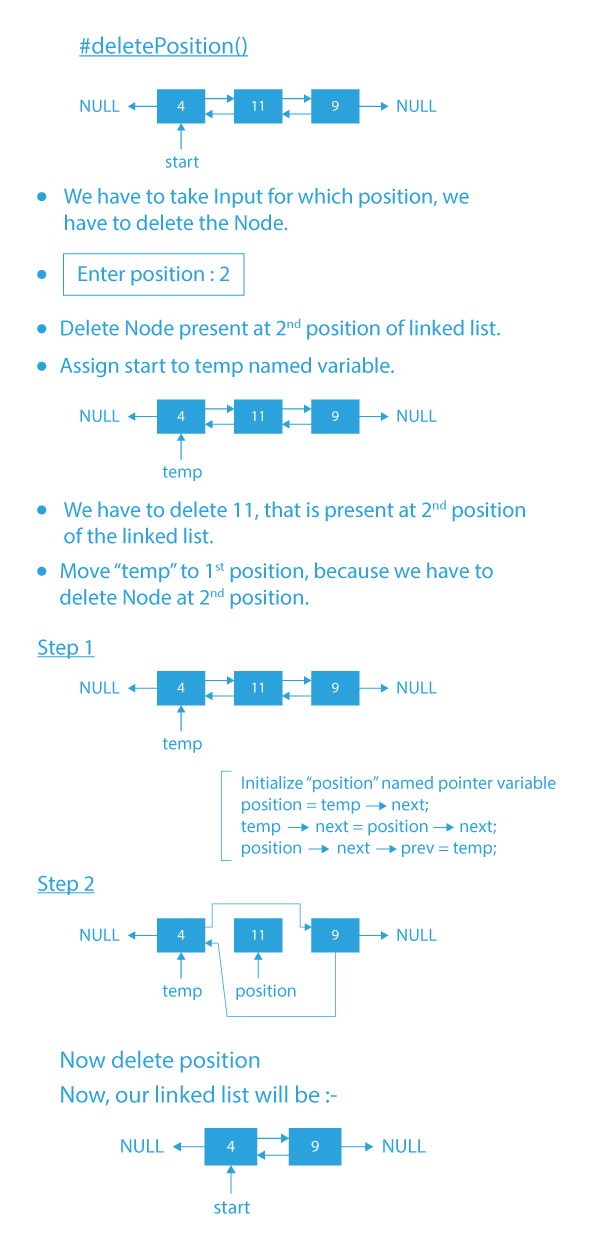
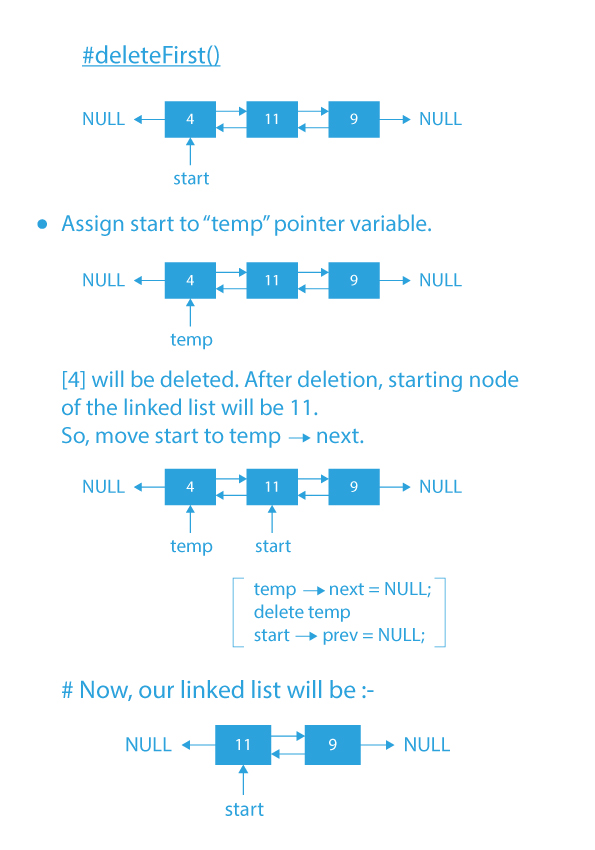
Code Implementation of Menu Driven Program of Operations of Doubly linked list
#include#include // Node Structure of the linked list struct node { int data; struct node *prev, *next; }; struct node* start = NULL; // Function to traverse and print the linked list void traverse(){ // List is empty // just return if (start == NULL) { printf("\nList is empty\n"); return; } // Else print the Node's Data struct node* temp; temp = start; while (temp != NULL) { printf("Data = %d\n", temp->data); temp = temp->next; } } // function to insert node at the front // of the linked list void insertAtFront(){ int data; struct node* temp; temp = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node)); printf("\nEnter number to be inserted: "); scanf("%d", &data); temp->data = data; temp->prev = NULL; // Pointer of temp will be assigned to start temp->next = start; start = temp; } // function to insert at the end of the linked list void insertAtEnd(){ int data; struct node *temp, *trav; temp = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node)); temp->prev = NULL; temp->next = NULL; printf("\nEnter number to be inserted: "); scanf("%d", &data); temp->data = data; temp->next = NULL; trav = start; // If start is NULL if (start == NULL) { start = temp; } // Changes Links else { while (trav->next != NULL) trav = trav->next; temp->prev = trav; trav->next = temp; } } // Function to insert at any given position in the linked list void insertAtPosition(){ int data, pos, i = 1; struct node *temp, *newnode; newnode = malloc(sizeof(struct node)); newnode->next = NULL; newnode->prev = NULL; // Enter the position and data printf("\nEnter position : "); scanf("%d", &pos); printf("\nEnter number to be inserted: "); scanf("%d", &data); newnode->data = data; temp = start; // If start==NULL, if (start == NULL) { start = newnode; newnode->prev = NULL; newnode->next = NULL; } // If position==1, else if (pos == 1) { newnode->next = start; newnode->next->prev = newnode; newnode->prev = NULL; start = newnode; } // Change links else { while (i < pos - 1) { temp = temp->next; i++; } newnode->next = temp->next; newnode->prev = temp; temp->next = newnode; temp->next->prev = newnode; } } // function to delete from the front of the linked list void deleteFirst(){ struct node* temp; if (start == NULL) printf("\nList is empty\n"); else { temp = start; start = start->next; if (start != NULL) start->prev = NULL; free(temp); } } // function to delete from the end // of the linked list void deleteEnd(){ struct node* temp; if (start == NULL) printf("\nList is empty\n"); temp = start; while (temp->next != NULL) temp = temp->next; if (start->next == NULL) start = NULL; else { temp->prev->next = NULL; free(temp); } } // function to delete from any given // position from the linked list void deletePosition(){ int pos, i = 1; struct node *temp, *position; temp = start; // If DLL is empty if (start == NULL) printf("\nList is empty\n"); // Otherwise else { // Position to be deleted printf("\nEnter position : "); scanf("%d", &pos); // If the position is the first node if (pos == 1) { position = start; start = start->next; if (start != NULL) { start->prev = NULL; } free(position); return; } // Traverse till position while (i < pos - 1) { temp = temp->next; i++; } // Change Links position = temp->next; if (position->next != NULL) position->next->prev = temp; temp->next = position->next; // Free memory free(position); } } int main(){ int choice; while (1) { printf("\n\t1 To see list\n"); printf("\t2 For insertion at" " starting\n"); printf("\t3 For insertion at" " end\n"); printf("\t4 For insertion at " "any position\n"); printf("\t5 For deletion of " "first element\n"); printf("\t6 For deletion of " "last element\n"); printf("\t7 For deletion of " "element at any position\n"); printf("\t8 To exit\n"); printf("\nEnter Choice :\n"); scanf("%d", &choice); switch (choice) { case 1: traverse(); break; case 2: insertAtFront(); break; case 3: insertAtEnd(); break; case 4: insertAtPosition(); break; case 5: deleteFirst(); break; case 6: deleteEnd(); break; case 7: deletePosition(); break; case 8: exit(1); break; default: printf("Incorrect Choice. Try Again \n"); continue; } } return 0; }
Output
1 To see list
2 For insertion at starting
3 For insertion at end
4 For insertion at any position
5 For deletion of first element
6 For deletion of last element
7 For deletion of element at any position
8 To exit
Enter Choice :
2
Enter number to be inserted: 4
1 To see list
2 For insertion at starting
3 For insertion at end
4 For insertion at any position
5 For deletion of first element
6 For deletion of last element
7 For deletion of element at any position
8 To exit
Enter Choice :
3
Enter number to be inserted: 11
1 To see list
2 For insertion at starting
3 For insertion at end
4 For insertion at any position
5 For deletion of first element
6 For deletion of last element
7 For deletion of element at any position
8 To exit
Enter Choice :
3
Enter number to be inserted: 9
1 To see list
2 For insertion at starting
3 For insertion at end
4 For insertion at any position
5 For deletion of first element
6 For deletion of last element
7 For deletion of element at any position
8 To exit
Enter Choice :
1
Data = 4
Data = 11
Data = 9Time Complexities
O(n):- traverse(), deleteEnd(), insertEnd(), deletePosition() and insertPosition().
O(1):- insertFront(), deleteFront().
Note: We are only given a pointer to the head of the doubly linked list.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the menu-driven program for all operations on a doubly linked list in C provides a user-friendly interface to perform various operations on a doubly linked list. The program enables users to manage a doubly linked list effectively through various essential operations. Users can create the list, insert elements at the beginning, end, or a specific position, delete elements, display the list’s contents, search for elements, and perform other crucial tasks. With a menu-based approach, the program streamlines the interaction with the doubly linked list, making it user-friendly and straightforward to manipulate the list.
FAQs related to Menu Driven Program For All Operations On Doubly Linked List in C :
Q1: What is a doubly linked list?
Ans. A doubly linked list is a type of linked list where each node contains two pointers, one pointing to the previous node and another pointing to the next node. This structure allows for efficient traversal in both directions.
Q2: Why use a menu-driven program for operations on a doubly linked list?
Ans. A menu-driven program provides a user-friendly interface that allows users to select desired operations without the need to remember complex commands or syntax. It simplifies the interaction and improves usability.
Q3: What operations can be performed on a doubly linked list using the menu-driven program?
Ans. The menu-driven program typically supports operations such as creating a list, inserting elements at various positions, deleting elements, searching for an element, displaying the contents of the list, counting the number of elements, reversing the list, and more.
Q4: How can I compile and run the menu-driven program in C?
Ans. To compile the program, you need a C compiler such as GCC. Save the program with a .c extension and use the command "gcc -o program_name program_name.c" to compile it. Then, run the compiled program using the command "./program_name".
Q5: What if I encounter errors or issues with the program?
Ans. If you encounter any errors or issues with the program, you can try debugging it by checking the code for errors, ensuring proper syntax and logic. Additionally, you can seek help from programming communities or forums to get assistance in resolving the problems you face.
Q6: Can I modify the program to add additional functionalities?
Ans. Yes, you can modify the program according to your requirements. The code can be extended to include additional functionalities or customize existing operations based on your specific needs. Be sure to understand the code structure and make necessary modifications while maintaining its integrity.


