Last Updated on July 31, 2023 by Mayank Dham

Linked lists are fundamental data structures used in computer science and programming to store and manage collections of data elements in a dynamic and flexible manner. One common operation when working with linked lists is to determine the size or the number of elements present in the list.
In this article, we will explore a program to find the size of linked list using various approaches in different programming languages, such as C, C++, Java, and Python. We will delve into the concepts of linked lists, node structures, and pointer manipulation to understand the underlying mechanisms behind counting the elements in the list.
Problem Statement
In this problem, we are given a doubly linked list, and we need to find the size of a doubly linked list.
Note: The linked list does not contain loop.
Problem Statement Understanding
Let’s first understand what a doubly linked list is.
In simple words, a doubly linked list can be defined as a linked data structure made up of nodes, which are sequentially linked records. Each node has three fields one data field and two link fields which are basically the pointers to the node before it and the node after it in the sequence. We can traverse through the doubly linked list in both ways as each of its node contains the address of previous as well as next node.
Now, let’s understand the problem statement with help of examples.
Suppose if we are given a doubly linked list:
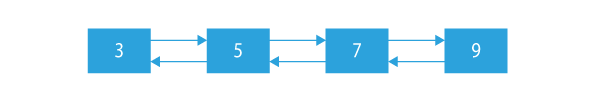
and we have to output its size.
We can see that the linked list contains total of 4 nodes so our output will be 4, as the size of linked list is equal to the number of nodes in the linked list.
If the linked list is:
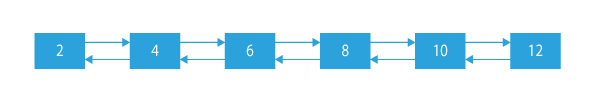
the size of the linked list is 6 equal to the number of the nodes.
Explanation The size of the linked list is equal to the number of nodes in the linked list.
Approach to find the size of a doubly linked list
The size of the linked list is equal to the count of the number of the nodes in the linked list.
To find the count of the nodes in the linked list:
- Initialize a counter variable to 0 and a temp pointer to the head of the linked list
- Using the temp pointer traverse the linked list until temp!=NULL and increment the counter variable by 1 for each node.
Finally when the temp==NULL the counter variable will have the size of the linked list.
Algorithm to find the size of a doubly linked list
- Initialize a variable ListSize to 0.
- Initialize a node pointer, temp = head.
- Do following while temp is not NULL
a) temp = temp -> next
b) ListSize++;
- Return ListSize.
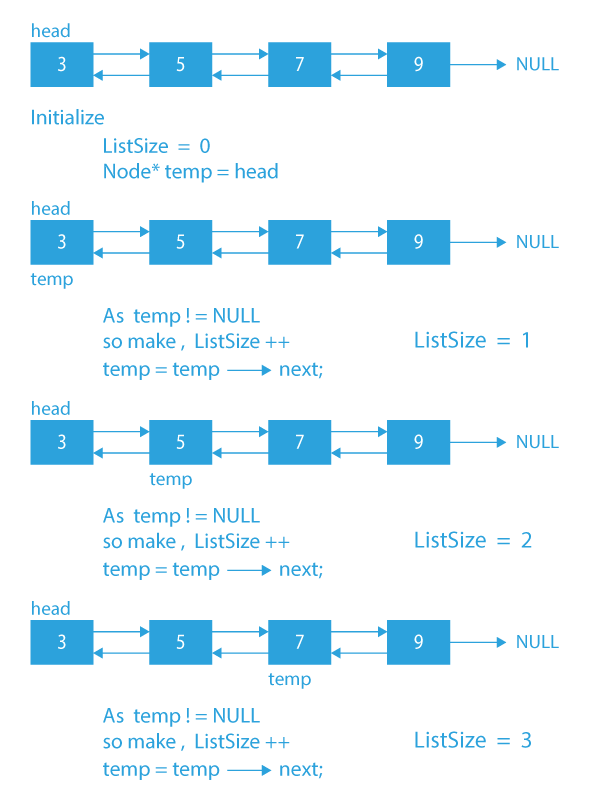
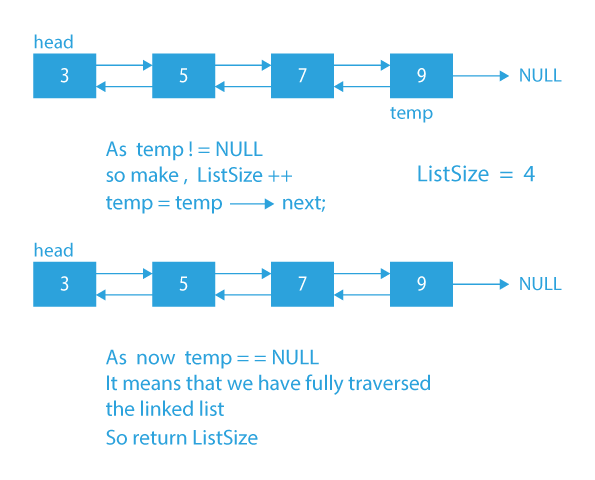
Dry Run to find the size of a doubly linked list
- Initialize a variable ListSize to 0.
- Initialize a node pointer, temp = head.
- Do following while temp is not NULL
a) temp = temp -> next
b) ListSize++; - Return ListSize.
Dry Run to find the size of a doubly linked list
Implementation to find the size of a doubly linked list
#includeusing namespace std; struct llNode { int data; struct llNode *next; struct llNode *prev; }; void push(struct llNode** head_ref, int data) { struct llNode* new_node = new llNode; new_node->data = data; new_node->next = (*head_ref); new_node->prev = NULL; if ((*head_ref) != NULL) (*head_ref)->prev = new_node ; (*head_ref) = new_node; } int SizeOfList(struct llNode *temp) { int ListSize = 0; while(temp != NULL) { ListSize++; temp = temp->next; } return ListSize; } int main() { struct llNode* head = NULL; push(&head, 9); push(&head, 7); push(&head, 5); push(&head, 3); cout <<"Size of the doubly linked list: "<< SizeOfList(head); return 0; }
Output
Size of the doubly linked list: 5
Time Complexity of the size of a doubly linked list: O(n), where n is the number of nodes in the linked list.
**Time Complexity of the size of a doubly linked list:** O(n) is the time complexity to write the Program to find size of linked list, where n is the number of nodes in the linked list.
**Conclusion**
In this article, we have tried to explain the most efficient algorithm for how to get the size of a doubly linked list. This problem is interesting as well as important from the interviewee’s point of view. If you want to solve more questions on Linked List, which is curated by our expert mentors at PrepBytes, you can follow this link Linked List.
## FAQ Related to Find the Size of Linked List
Here are some FAQs related to the program to find the size of linked list.
**1. Can the size of a linked list change during program execution?**
Yes, the size of a linked list can change dynamically as you add or remove elements from the list during program execution.
**2. Why is finding the size of a linked list important?**
Determining the size of a linked list is crucial for understanding the amount of data stored in the list and for performing various operations efficiently, such as traversal and searching.
**3. How can I find the size of a linked list in C?**
In C, you can find the size of a linked list by iterating through the list and counting the number of nodes using a loop or recursion.
**4. Is there any standard library function available to find the size of a linked list in programming languages like Java or Python?**
No, there is no built-in standard library function to find the size of a linked list in Java or Python. You will need to implement the size calculation logic manually.
**5. What is the time complexity of finding the size of a linked list?**
The time complexity of finding the size of a linked list is O(n), where n is the number of nodes in the list. This is because you need to traverse the entire list to count the nodes.
**6. Can I find the size of a circular linked list using the same method as a singly linked list?**
Yes, you can find the size of a circular linked list using the same method as a singly linked list. However, you need to take care of the termination condition to avoid an infinite loop.


