Last Updated on November 18, 2022 by Prepbytes

In the following article, we are going to look into an approach for searching in doubly linked list. We already know that doubly linked list requires more space as it’s node contains three parts. One is data part and the other two are pointers. So lets just see how search in doubly linked list works.
Problem Statement for search element in doubly linked list
In this problem, we are given a Doubly Linked List, and we need to search for a node with value X in the list and return its position.
Problem Statement Understanding for searching in doubly linked list
Let’s try to understand the problem statement with the help of an example.
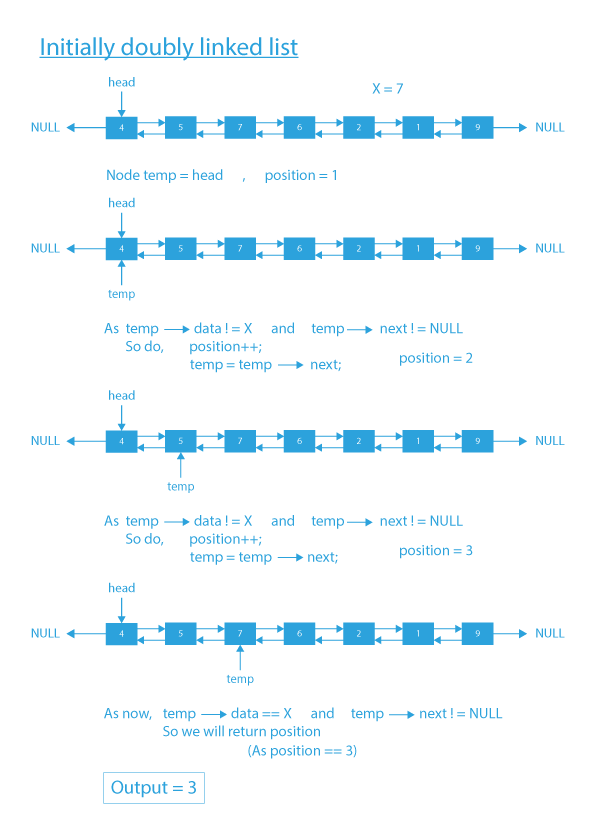
If the given doubly linked list is head ↔ 4 ↔ 5 ↔ 7 ↔ 6 ↔ 2 ↔ 1 ↔ 9 and X = 7.
- According to the problem statement, we will have to search for the node with value X in the list, and finally, after finding the node, we have to return its position in the list.
- We can clearly see that node with value 7 is present in the list, and this node is at 3rd position (considering one based indexing) in the list.
- So finally, we will output 3, as 3 is the position of a node with value X = 7 in the given list.
Input: head ↔ 4 ↔ 5 ↔ 7 ↔ 6 ↔ 2 ↔ 1 ↔ 9, X(element to be searched) = 7
Output: 3
Also, there can be multiple nodes with value X in the list, so that’s why we will return the position of the first node with value X in the list.
Note: If there is no node with the value of X in the list, the output will be -1.
Now I think the problem statement is clear, so let’s see how we can approach it.
Let’s move to the approach section.
Approach for search element in doubly linked list
In order to find an element X in the given doubly linked list:
- We need to traverse the list until either the node is null or we have found the node with value X which we were searching for.
- Also, we need a variable position that will keep the count of the elements we have visited so far.
- Then finally, we will return the location of the element X in our list which will be given by the variable position.
Algorithm for search in doubly linked list
- First, we need to create a variable position that will keep track of number of nodes traversed.
- Then using a pointer, say, temp, we will traverse the given list till the next node of the temp is null, or we found the element we were searching for.
- Then we will check if the current node’s data is equal to the element we were searching for or not.
- If temp.data == X, our position variable will give the location of the element to be searched for and we will output it.
- Else, it means that there is no node with value X in the given list, so we will output -1.
Dry Run for search element in doubly linked list
Code Implementation search in doubly linked list
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
// Structure of a node of
// the doubly linked list
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node* next;
struct Node* prev;
};
// Function to insert a node at the
// beginning of the Doubly Linked List
void push(struct Node** head_ref, int new_data)
{
struct Node* new_node
= (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
new_node->data = new_data;
new_node->prev = NULL;
new_node->next = (*head_ref);
if ((*head_ref) != NULL) {
(*head_ref)->prev = new_node;
}
(*head_ref) = new_node;
}
// Function to find the position of
// an integer in doubly linked list
int search(struct Node** head_ref, int x)
{
struct Node* temp = *head_ref;
int pos = 0;
while (temp->data != x
&& temp->next != NULL) {
pos++;
temp = temp->next;
}
if (temp->data != x)
return -1;
return (pos + 1);
}
int main()
{
struct Node* head = NULL;
int X = 8;
// Create the doubly linked list
// 18 <-> 15 <-> 8 <-> 9 <-> 14
push(&head, 14);
push(&head, 9);
push(&head, 8);
push(&head, 15);
push(&head, 18);
printf("%d ",search(&head, X));
return 0;
}
#include <bits stdc++.h="">
using namespace std;
struct DLLNode {
int data;
DLLNode* next;
DLLNode* prev;
};
void push(DLLNode** head, int new_data){
DLLNode* new_node = (DLLNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct DLLNode));
new_node->data = new_data;
new_node->prev = NULL;
new_node->next = (*head);
if ((*head) != NULL) {
(*head)->prev = new_node;
}
(*head) = new_node;
}
int search_the_element(DLLNode** head, int X){
DLLNode* temp = *head;
int position = 0;
while (temp->data != X && temp->next != NULL) {
position++;
temp = temp->next;
}
if (temp->data != X)
return -1;
return (position + 1);
}
int main()
{
DLLNode* head = NULL;
int X = 7;
push(&head, 9);
push(&head, 1);
push(&head, 2);
push(&head, 6);
push(&head, 7);
push(&head, 5);
push(&head, 4);
cout<<search_the_element(&head, x)
return=0;
public class Prepbytes {
static class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node prev;
};
static Node push(Node head_ref, int new_data) {
Node new_node = new Node();
new_node.data = new_data;
new_node.prev = null;
new_node.next = head_ref;
if (head_ref != null) {
head_ref.prev = new_node;
}
head_ref = new_node;
return head_ref;
}
static int search(Node head_ref, int x) {
Node temp = head_ref;
int position = 1;
while (temp.data != x && temp.next != null) {
position++;
temp = temp.next;
}
if (temp.data != x)
return -1;
return position;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node head = null;
int X = 7;
head = push(head, 9);
head = push(head, 1);
head = push(head, 2);
head = push(head, 6);
head = push(head, 7);
head = push(head, 5);
head = push(head, 4);
System.out.print(search(head, X));
}
}
class Node: def __init__(self): self.data = 0 self.next = None self.prev = None def push(head_ref, new_data): new_Node = Node() new_Node.data = new_data new_Node.prev = None new_Node.next = head_ref if (head_ref != None): head_ref.prev = new_Node head_ref = new_Node return head_ref def search(head_ref, x): temp = head_ref position = 0 while (temp.data != x and temp.next != None): position+=1 temp = temp.next if (temp.data != x): return -1 return (position + 1) if __name__ == '__main__': head = None X = 7 head = push(head, 9) head = push(head, 1) head = push(head, 2) head = push(head, 6) head = push(head, 7) head = push(head, 5) head = push(head, 4) print(search(head, X))
Output
3
Time Complexity: O(n), where n is the total number of nodes in the Doubly Linked List.
Conclusion
So, We did an understandable approach on how searching in doubly linked list works. We have tried to cover all the aspects of the approach. If you want to solve more questions on Linked List, which are curated by our expert mentors at PrepBytes, you can follow this link Linked List.
FAQs
- Can we apply binary search on doubly linked list?
- What is searching in linked list?
We can apply binary search on doubly linked list with the time complexity of O(nlogn), but in an efficient approach we can use it with a time complexity of O(n).
The process of finding a desired or wanting element or whether to check whether the element is present in the list or not by traversing through it is called searching.


